4 The Telencephalon
In this laboratory session, we will study the anatomy of the human telencephalon. The cerebrum or telencephalon is a large part of the brain containing the cerebral cortex (of the two cerebral hemispheres), as well as several subcortical structures, including the hippocampus, basal ganglia, and olfactory bulb. In the human brain, the cerebrum is the uppermost region of the central nervous system. The prosencephalon or forebrain is the embryonic structure from which the cerebrum develops prenatally. In mammals, the dorsal telencephalon, or pallium, develops into the cerebral cortex, and the ventral telencephalon, or subpallium, becomes the basal ganglia. The cerebrum is also divided into approximately symmetric left and right cerebral hemispheres.
Below, you will be presented with a number of figures and asked to label or color certain structures in each figure.
4.1 A Series Of Coronal Sections Of A Human Brain
In Figure 4.1, label the following structures:
- The cingulate sulcus
- The cingulate gyrus
- The corpus callosum
- The lateral ventricle
- The caudate nucleus
- The insula
- The lateral sulcus
- The superior temporal gyrus
- The superior temporal sulcus
- The middle temporal gyrus
- The middle temporal sulcus
- The inferior temporal gyrus
- The inferior temporal sulcus
- The putamen
- The nucleus accumbens
- The optic nerves (left and right)
- The septum pelucidum
- The septal nuclei
- The internal capsule
- The external capsule
- The entorhinal cortex
- The parahippocampal gyrus
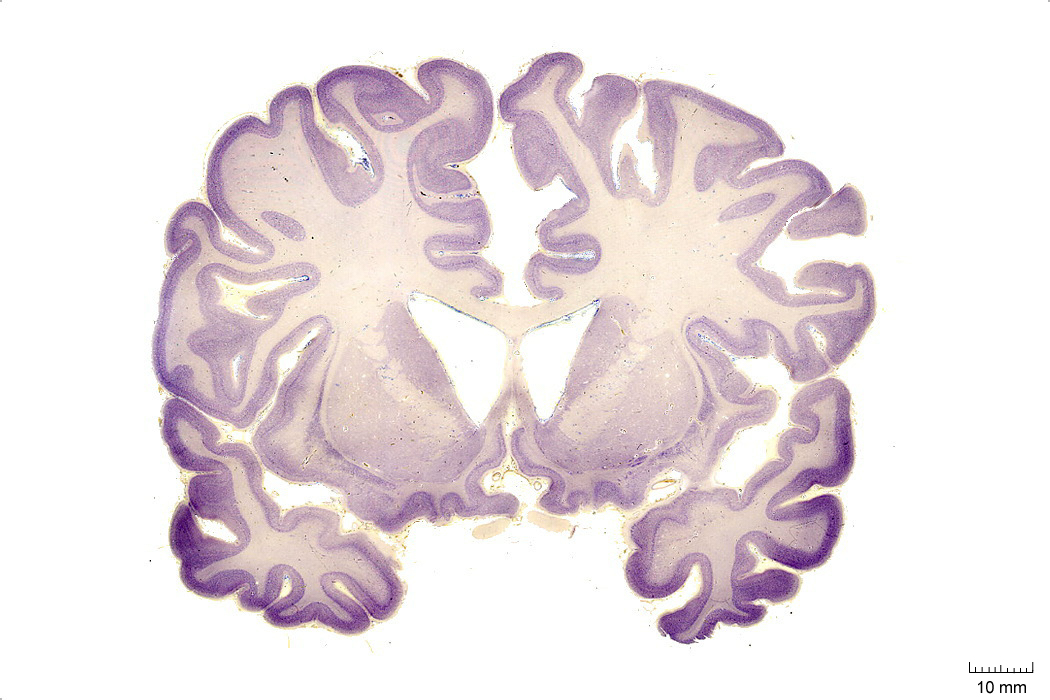
Figure 4.1: Coronal section from The Human Brain Atlas at the Michigan State University Brain Biodiveristy Bank which acknowledges their support from the National Science Foundation.
In Figure 4.2, label the following structures:
- The cingulate sulcus
- The cingulate gyrus
- The corpus callosum
- The fornix
- The lateral ventricle
- The choroid plexus
- The anterior commissure
- The insula
- The lateral sulcus
- The superior temporal gyrus
- The superior temporal sulcus
- The middle temporal gyrus
- The middle temporal sulcus
- The inferior temporal gyrus
- The inferior temporal sulcus
- The putamen
- The preoptic area
- The optic chiasm
- The infundibular stalk
- A pigment epithelial cell with extended proces
- The 3d ventricle
- The internal capsule
- The external capsule
- The claustrum
- The globus pallidus
- The anterior commissure
- The amygdala
- The entorhinal cortex
- The parahippocampal gyrus
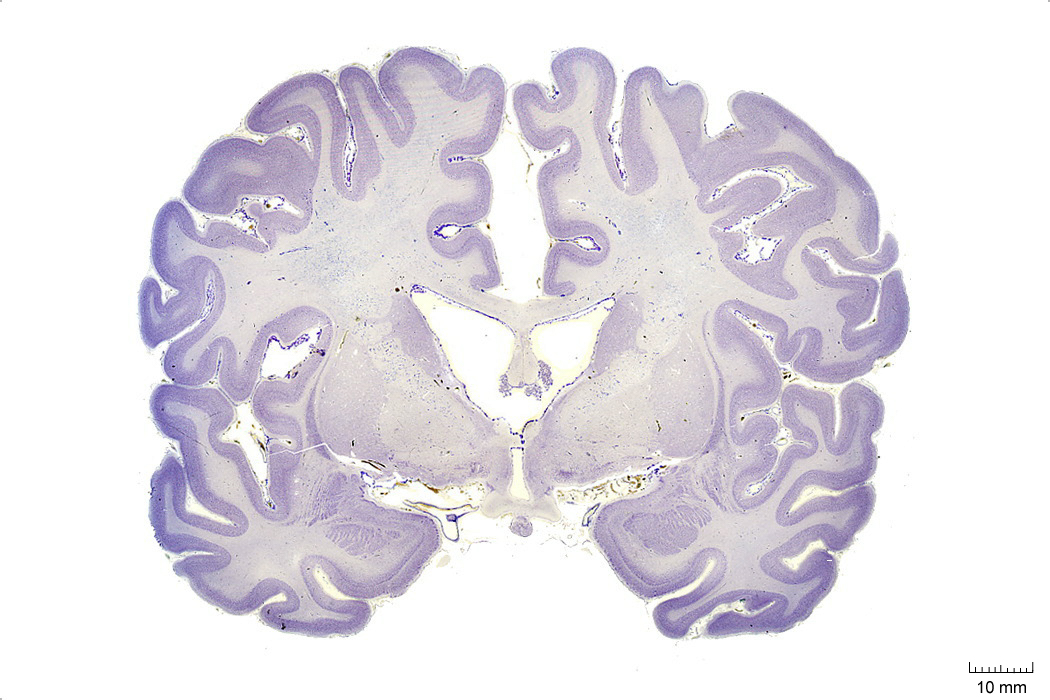
Figure 4.2: Coronal section from The Human Brain Atlas at the Michigan State University Brain Biodiveristy Bank which acknowledges their support from the National Science Foundation.
In Figure 4.3, label the following structures:
- The cingulate sulcus
- The cingulate gyrus
- The corpus callosum
- The fornix
- The lateral ventricle
- The choroid plexus
- The caudate nucleus
- The thalamus
- The insula
- The lateral sulcus
- The superior temporal gyrus
- The superior temporal sulcus
- The middle temporal gyrus
- The middle temporal sulcus
- The inferior temporal gyrus
- The inferior temporal sulcus
- The putamen
- The hippocampus
- The 3d ventricle
- The internal capsule
- The external capsule
- The claustrum
- The globus pallidus
- The fornix
- The optic tract
- The hypothalamus
- The lateral ventricle
- The entorhinal cortex
- The parahippocampal gyrus
- The amygdaloid nuclei:
- medial
- central
- cortical
- basomedial
- basolateral
- lateral
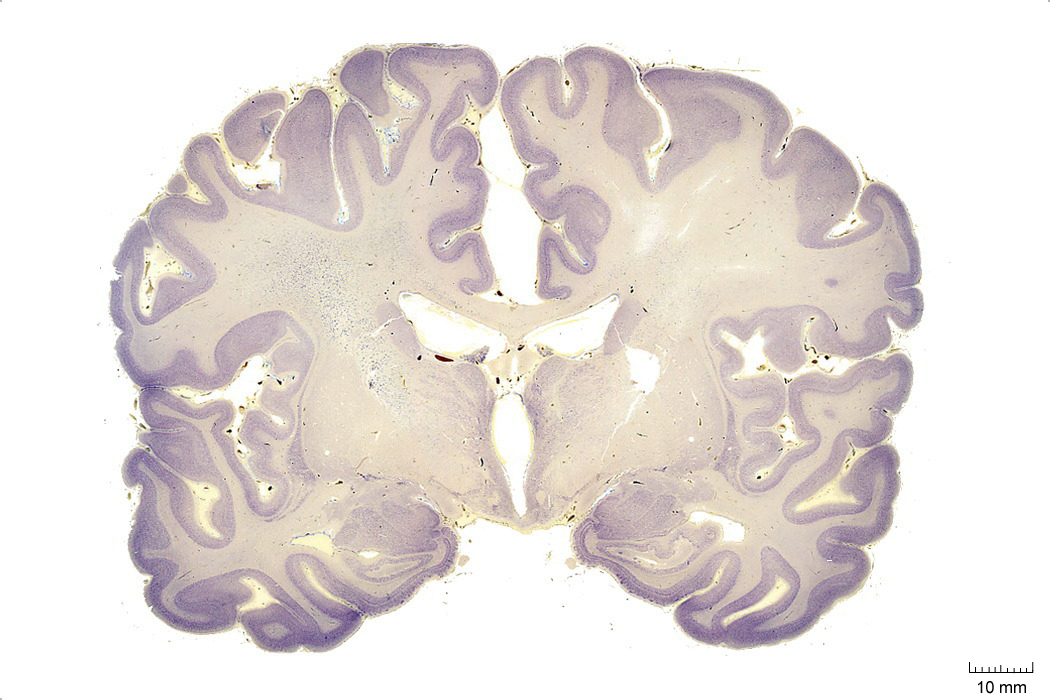
Figure 4.3: Coronal section from The Human Brain Atlas at the Michigan State University Brain Biodiveristy Bank which acknowledges their support from the National Science Foundation.
In Figure 4.4, label the following structures:
- The cingulate sulcus
- The cingulate gyrus
- The corpus callosum
- The fornix
- The lateral ventricle
- The choroid plexus
- The caudate nucleus
- The thalamus
- The insula
- The lateral sulcus
- The superior temporal gyrus
- The superior temporal sulcus
- The middle temporal gyrus
- The middle temporal sulcus
- The inferior temporal gyrus
- The inferior temporal sulcus
- The putamen
- The hippocampus
- The dentate gyrus
- The zona incerta
- The substantia nigra
- The 3d ventricle
- The thalamus
- The internal capsule
- The external capsule
- The claustrum
- The globus pallidus
- The optic tract
- The lateral ventricle
- The subthalamic nucleus
- The entorhinal cortex
- The parahippocampal gyrus
- The cerebral peduncle
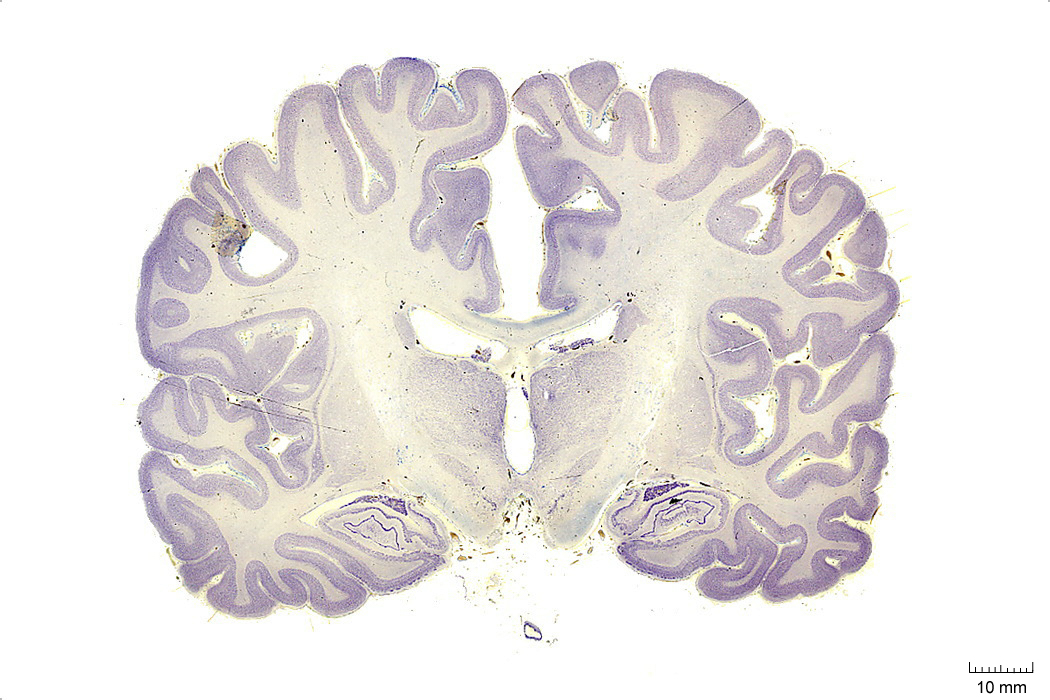
Figure 4.4: Coronal section from The Human Brain Atlas at the Michigan State University Brain Biodiveristy Bank which acknowledges their support from the National Science Foundation.
In Figure 4.5, label the following structures:
- The cingulate gyrus
- The corpus callosum
- The fornix
- The lateral ventricle
- The choroid plexus
- The caudate nucleus
- The thalamus
- The insula
- The lateral sulcus
- The superior temporal gyrus
- The superior temporal sulcus
- The middle temporal gyrus
- The middle temporal sulcus
- The inferior temporal gyrus
- The inferior temporal sulcus
- The putamen
- The hippocampus
- The dentate gyrus
- The red nucleus
- The substantia nigra
- The 3d ventricle
- The thalamus
- The internal capsule
- The external capsule
- The pons
- The zona incerta
- The globus pallidus
- The optic tract
- The lateral ventricle
- The subthalamic nucleus
- The entorhinal cortex
- The parahippocampal gyrus
- The cerebral peduncle
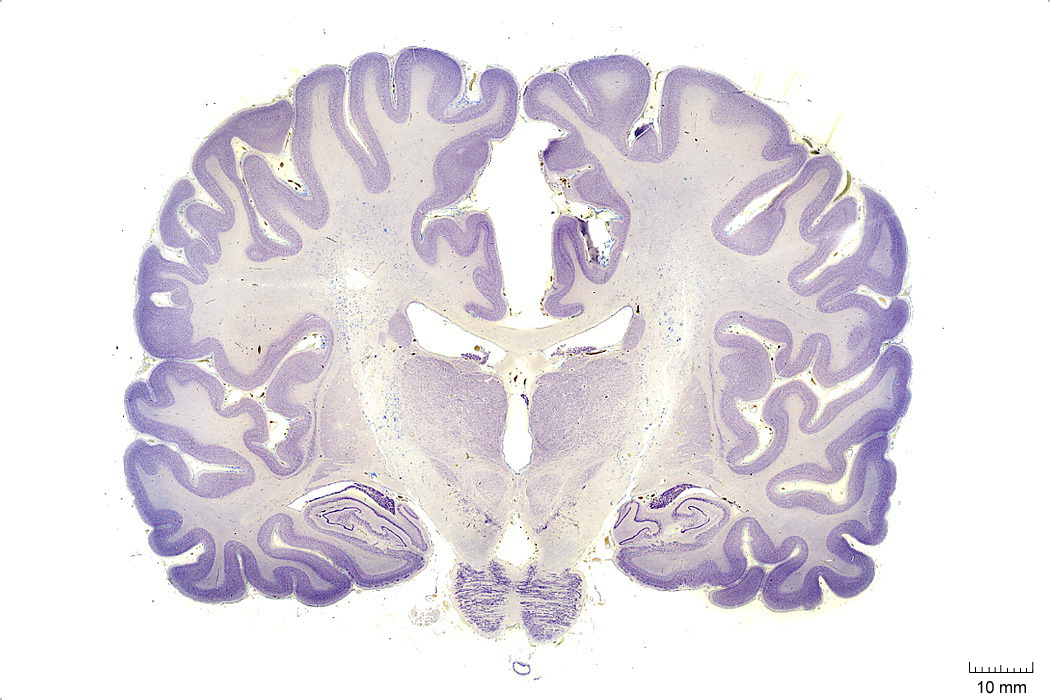
Figure 4.5: Coronal section from The Human Brain Atlas at the Michigan State University Brain Biodiveristy Bank which acknowledges their support from the National Science Foundation.
In Figure 4.6, label the following structures:
- The cingulate gyrus
- The corpus callosum
- The fornix
- The lateral ventricle
- The choroid plexus
- The caudate nucleus
- The insula
- The lateral sulcus
- The superior temporal gyrus
- The superior temporal sulcus
- The middle temporal gyrus
- The middle temporal sulcus
- The inferior temporal gyrus
- The inferior temporal sulcus
- The putamen
- The hippocampus
- The dentate gyrus
- The red nucleus
- The substantia nigra
- The decussation of the superior cerebellar peduncle
- The habenula
- The pineal gland
- The medial geniculate nucleus
- The lateral geniculate nucleus
- The cerebral peduncle
- The lateral ventricle
- The entorhinal cortex
- The parahippocampal gyrus
- The posterior commissure
- The cerebral aqueduct
- The pons
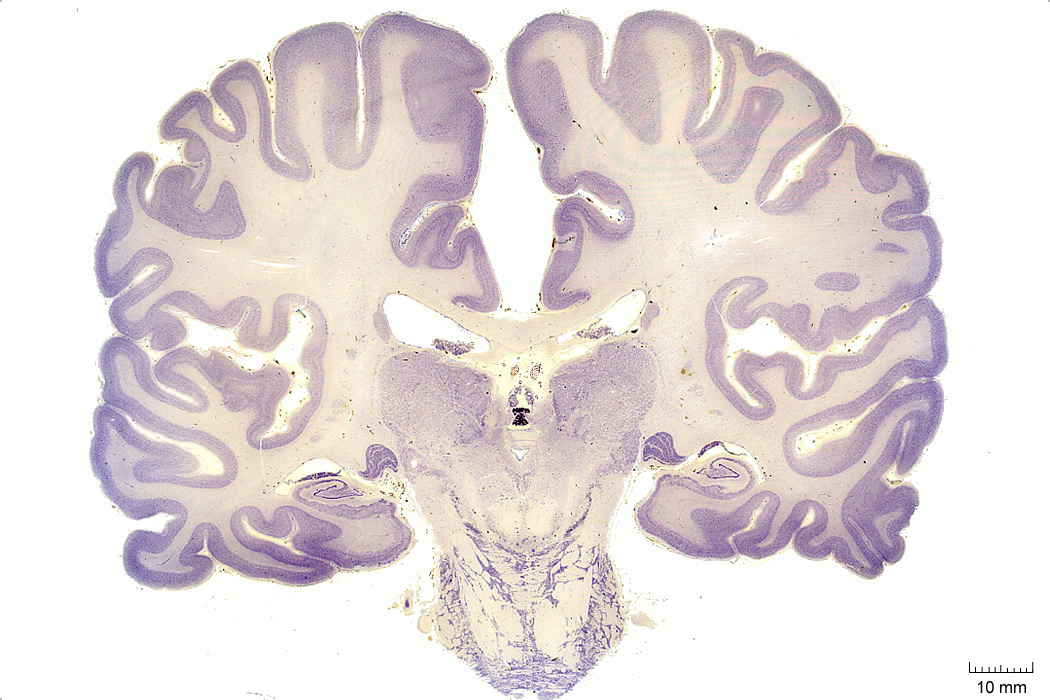
Figure 4.6: Coronal section from The Human Brain Atlas at the Michigan State University Brain Biodiveristy Bank which acknowledges their support from the National Science Foundation.
In Figure 4.7, label the following structures:
- The cingulate gyrus
- The corpus callosum
- The fornix
- The lateral ventricle
- The choroid plexus
- The caudate nucleus
- The thalamus
- The insula
- The lateral sulcus
- The superior temporal gyrus
- The superior temporal sulcus
- The middle temporal gyrus
- The middle temporal sulcus
- The inferior temporal gyrus
- The inferior temporal sulcus
- The putamen
- The hippocampus
- The dentate gyrus
- The pineal gland
- The periaqueductal grey matter
- The superior cerebellar peduncle
- The cerebral aqueduct
- The pulvinar
- The superior colliculus
- The lateral ventricle
- The oculomotor nucleus
- The medial longitudinal fasciculus
- The parahippocampal gyrus
- The cerebellum
- The pons
- The pyramidal tract
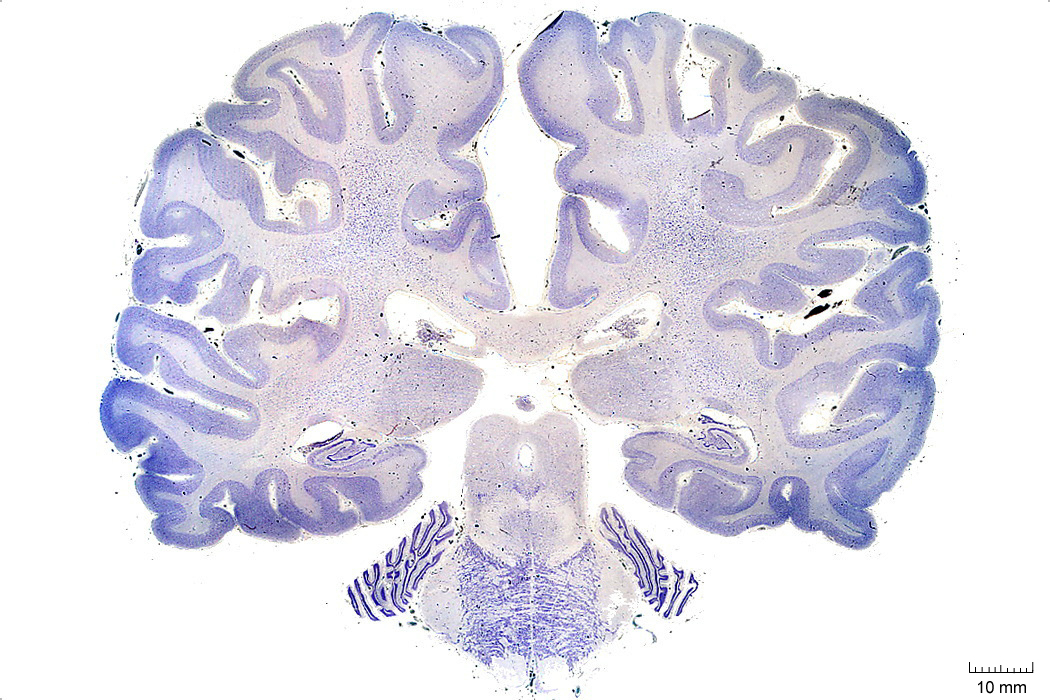
Figure 4.7: Coronal section from The Human Brain Atlas at the Michigan State University Brain Biodiveristy Bank which acknowledges their support from the National Science Foundation.
In Figure 4.8, label the following structures:
- The cingulate gyrus
- The corpus callosum
- The fornix
- The choroid plexus
- The caudate nucleus
- The insula
- The lateral sulcus
- The middle temporal gyrus
- The middle temporal sulcus
- The inferior temporal gyrus
- The inferior temporal sulcus
- The hippocampus
- The dentate gyrus
- The superior cerebellar peduncle
- The inferior olive
- The 4th ventricle
- The lateral ventricle
- The inferior colliculus
- The parahippocampal gyrus
- The medial longitudinal fasciculus
- The cerebellum
- The middle cerebellar peduncle
- The pontine reticular formation
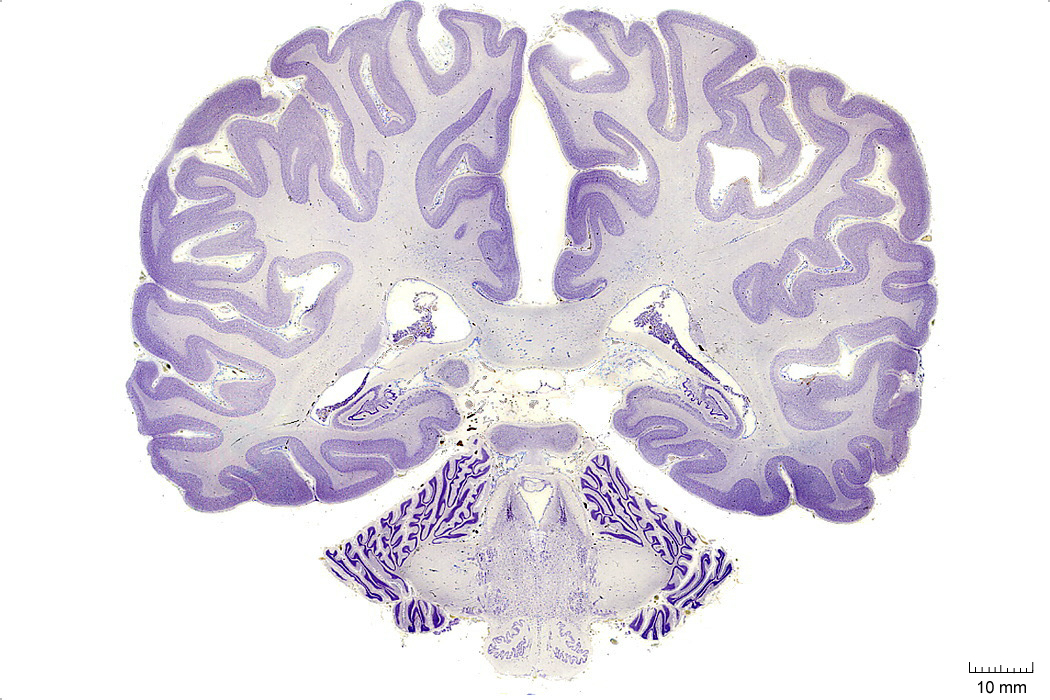
Figure 4.8: Coronal section from The Human Brain Atlas at the Michigan State University Brain Biodiveristy Bank which acknowledges their support from the National Science Foundation.
In Figure 4.9, label the following structures:
- The dentate gyrus
- The medial vestibular nucleus
- The nucleus of the solitary tract
- The solitary tract
- The lateral ventricle
- The 4th ventricle
- The inferior cerebellar peduncle
- The inferior olive
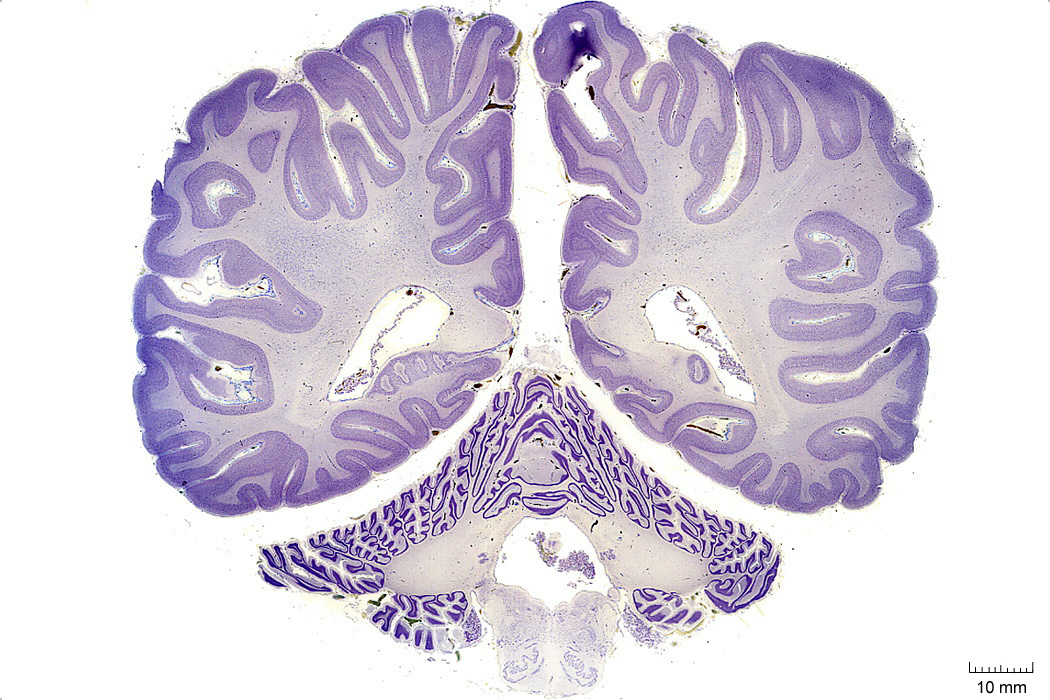
Figure 4.9: Coronal section from The Human Brain Atlas at the Michigan State University Brain Biodiveristy Bank which acknowledges their support from the National Science Foundation.
In Figure 4.10, label the following structures:
- The lateral ventricle
- The vermis
- The cerebellum
- The inferior olive
- The spinal cord
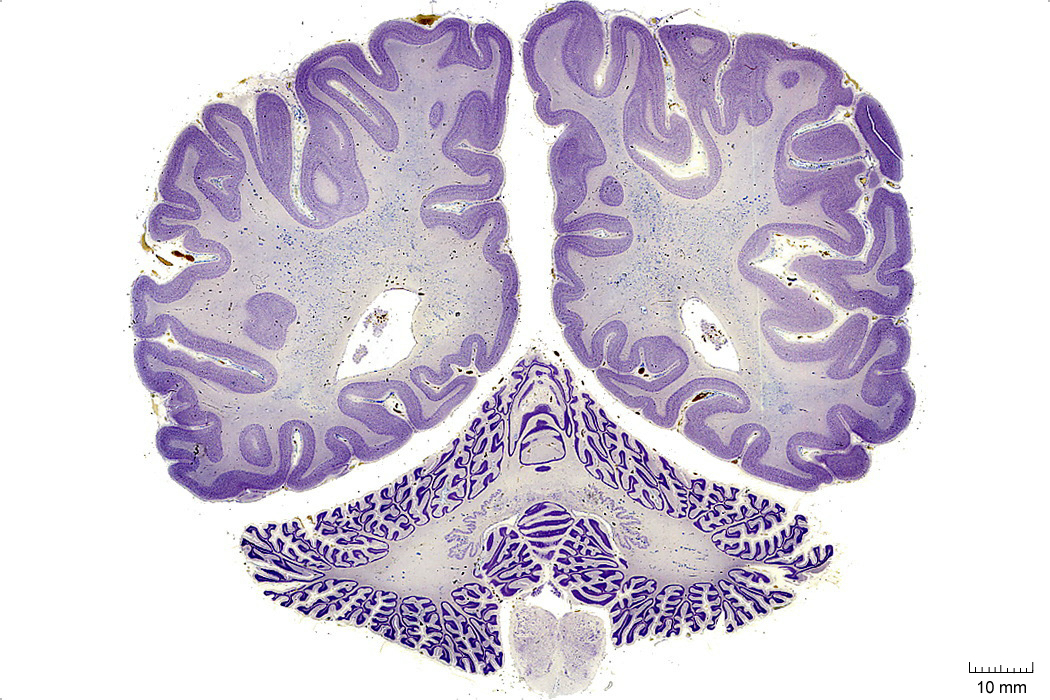
Figure 4.10: Coronal section from The Human Brain Atlas at the Michigan State University Brain Biodiveristy Bank which acknowledges their support from the National Science Foundation.
In Figure 4.11, label the following structures:
- The calcarine sulcus
- The striate cortex (primary visual cortex)
- The vermis
- The cerebellum
- The spinal cord:
- dorsal horn
- ventral horn
- dorsal column
- lateral column
- ventral column
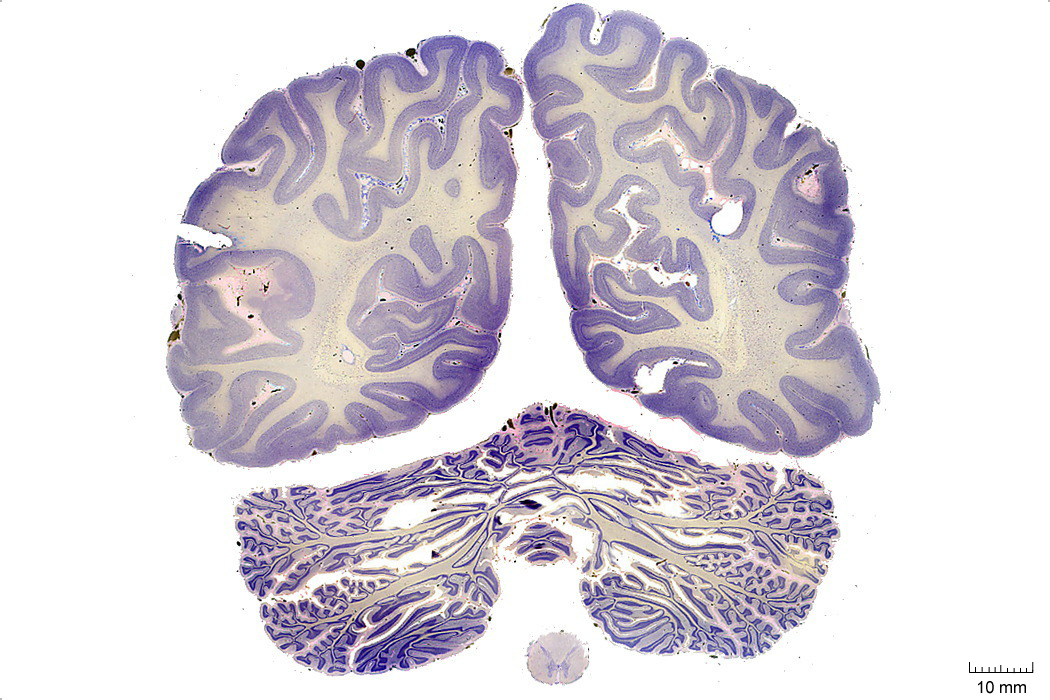
Figure 4.11: Coronal section from The Human Brain Atlas at the Michigan State University Brain Biodiveristy Bank which acknowledges their support from the National Science Foundation.
4.2 A Series Of Sagittal Sections Of A Human Brain
In Figure 4.12, label the following structures:
- The lateral sulcus
- The superior temporal sulcus
- The middle temporal sulcus
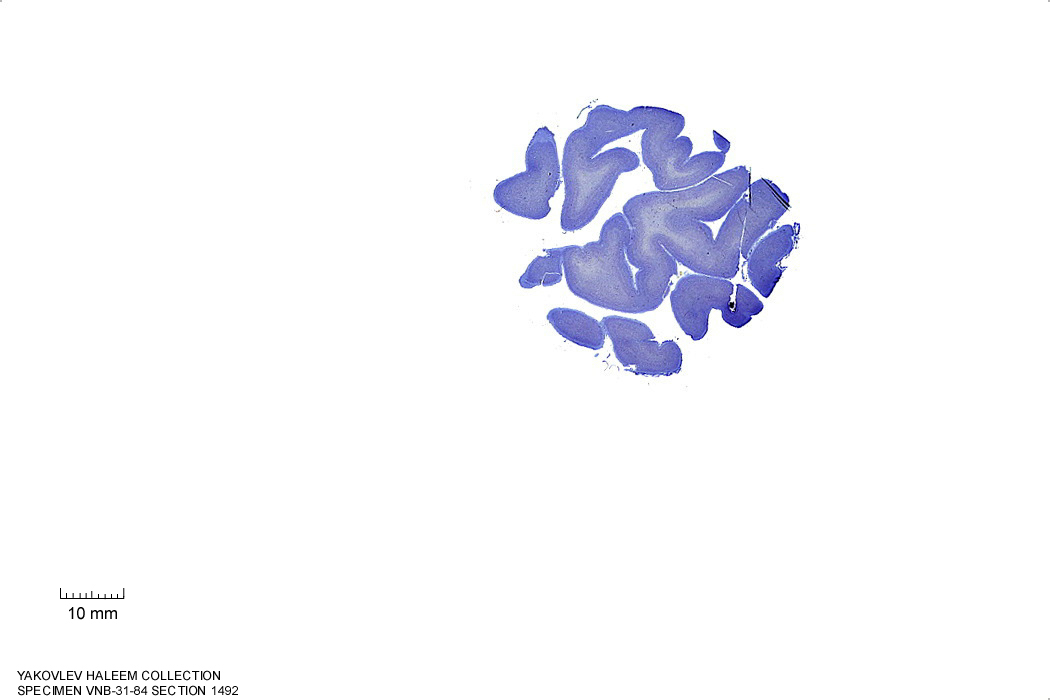
Figure 4.12: Sagittal section from The Human Brain Atlas at the Michigan State University Brain Biodiveristy Bank which acknowledges their support from the National Science Foundation.
In Figure 4.13, label the following structures:
- The lateral sulcus
- The superior temporal gyrus
- The superior temporal sulcus
- The middle temporal sulcus
- The inferior temporal sulcus
- The inferior temporal gyrus
- The central sulcus
- The precentral gyrus
- The postcentral gyrus
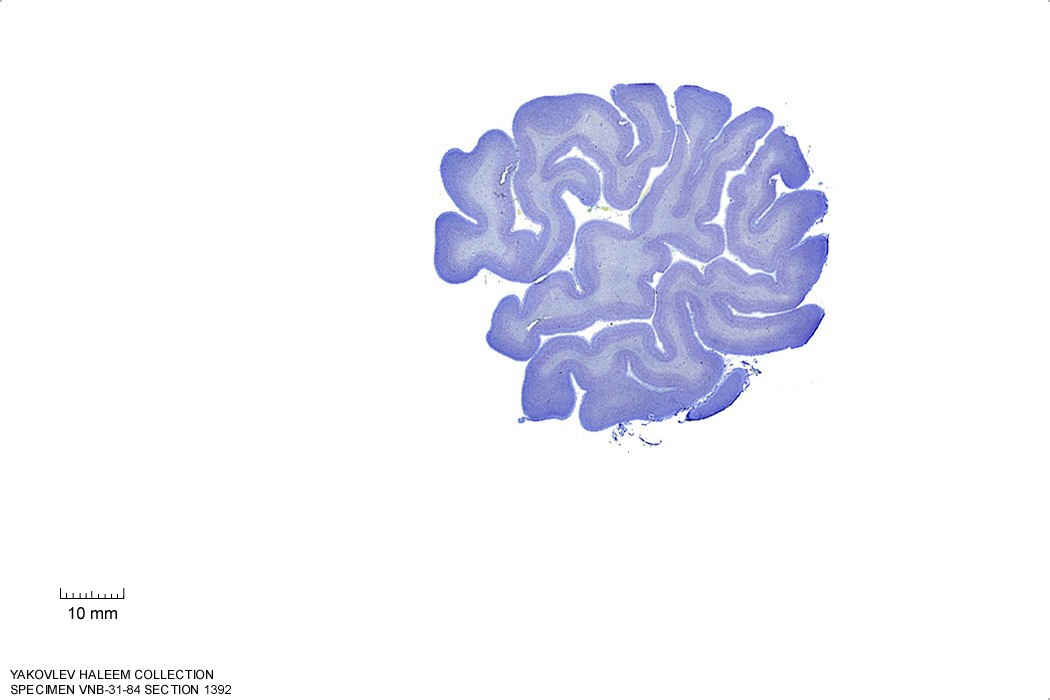
Figure 4.13: Sagittal section from The Human Brain Atlas at the Michigan State University Brain Biodiveristy Bank which acknowledges their support from the National Science Foundation.
In Figure 4.14, label the following structures:
- The middle frontal gyrus
- The inferior frontal sulcus
- The inferior frontal gyrus
- oprecular part
- triangular part
- orbital part
- The lateral sulcus
- The superior temporal gyrus
- The superior temporal sulcus
- The middle temporal sulcus
- The inferior temporal sulcus
- The inferior temporal gyrus
- The precentral sulcus
- The precentral gyrus
- The central sulcus
- The postcentral gyrus
- The postcentral sulcus
- The transverse tremporal sulci
- Heschl’s gyrus
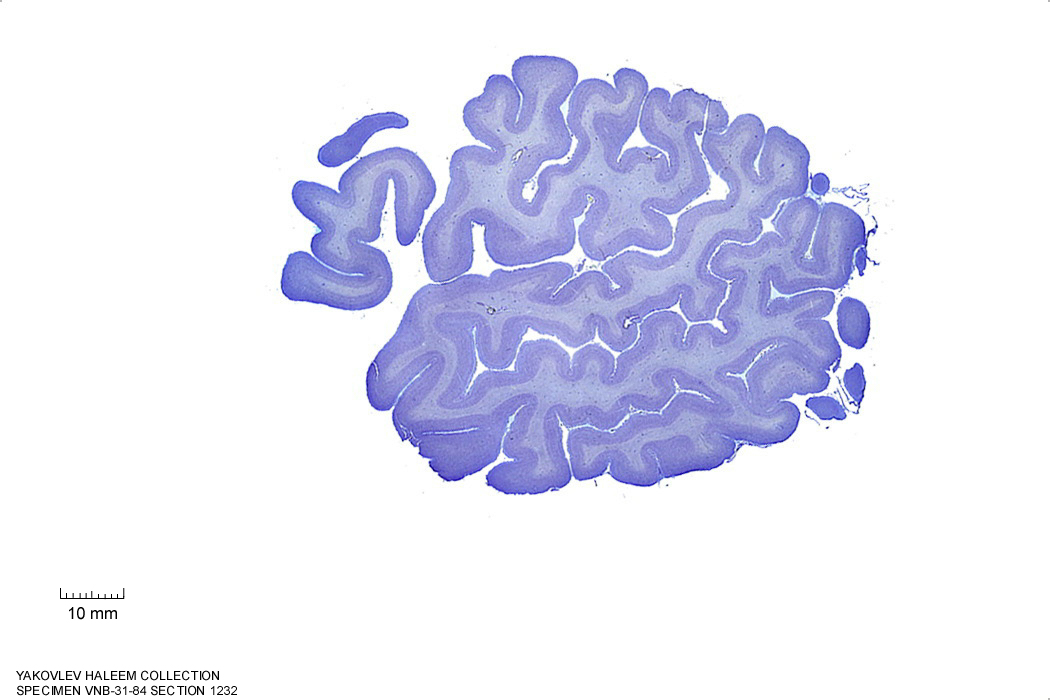
Figure 4.14: (ref:s1232)
In Figure 4.15, label the following structures:
- The insula
- The lateral sulcus
- The cerebellum
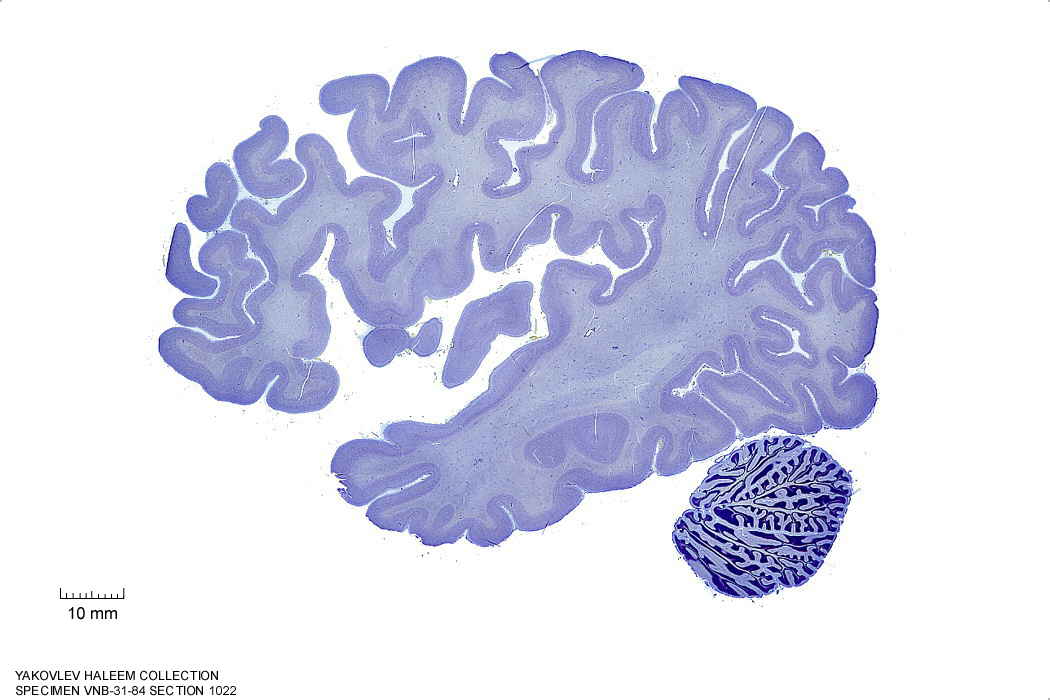
Figure 4.15: Sagittal section from The Human Brain Atlas at the Michigan State University Brain Biodiveristy Bank which acknowledges their support from the National Science Foundation.
In Figure 4.16, label the following structures:
- The insula
- The claustrum
- The tail of the caudate nucleus
- The hippocampus
- The lateral ventricle
- The cerebellum
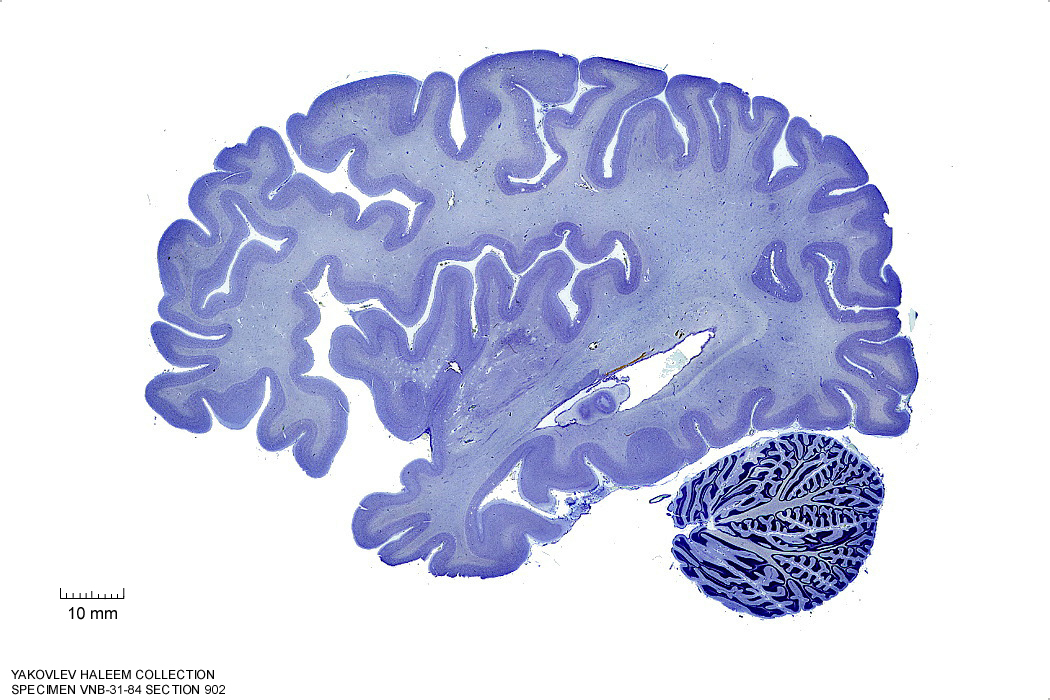
Figure 4.16: Sagittal section from The Human Brain Atlas at the Michigan State University Brain Biodiveristy Bank which acknowledges their support from the National Science Foundation.
In Figure 4.17, label the following structures:
- The external capsule
- The internal capsule
- The claustrum
- The putamen
- The anterior commissure
- The tail of the caudate nucleus
- The hippocampus
- The dentate gyrus
- The cerebellum
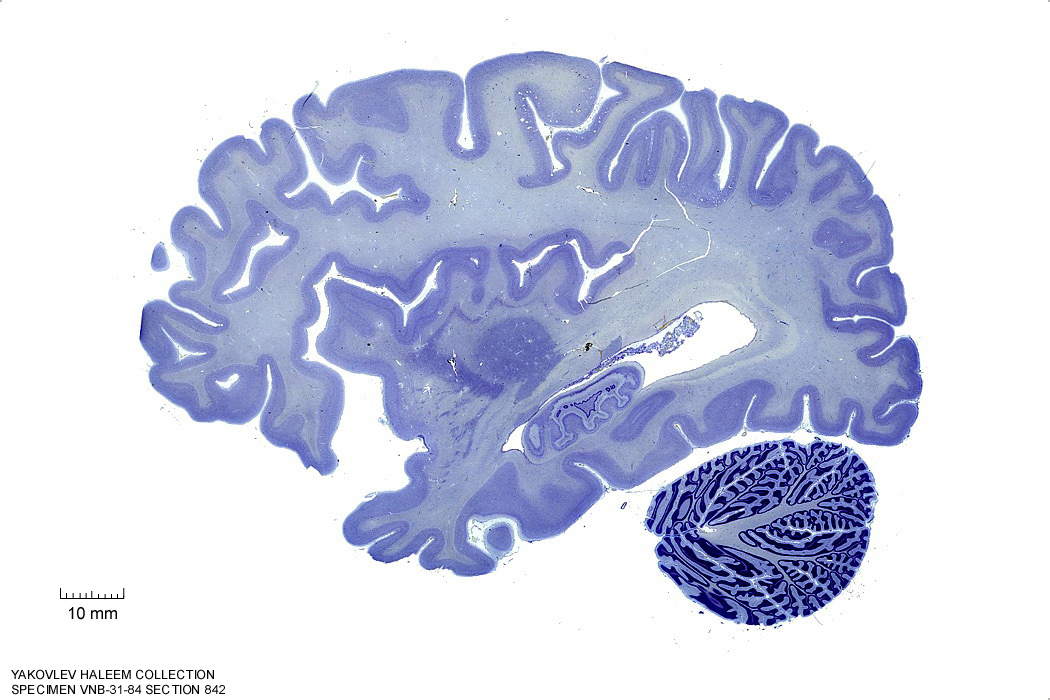
Figure 4.17: Sagittal section from The Human Brain Atlas at the Michigan State University Brain Biodiveristy Bank which acknowledges their support from the National Science Foundation.
In Figure 4.18, label the following structures:
- The external capsule
- The internal capsule
- The claustrum
- The putamen
- The anterior commissure
- The amygdala
- The optic tract
- The tail of the caudate nucleus
- The hippocampus
- The dentate gyrus
- The cerebellum
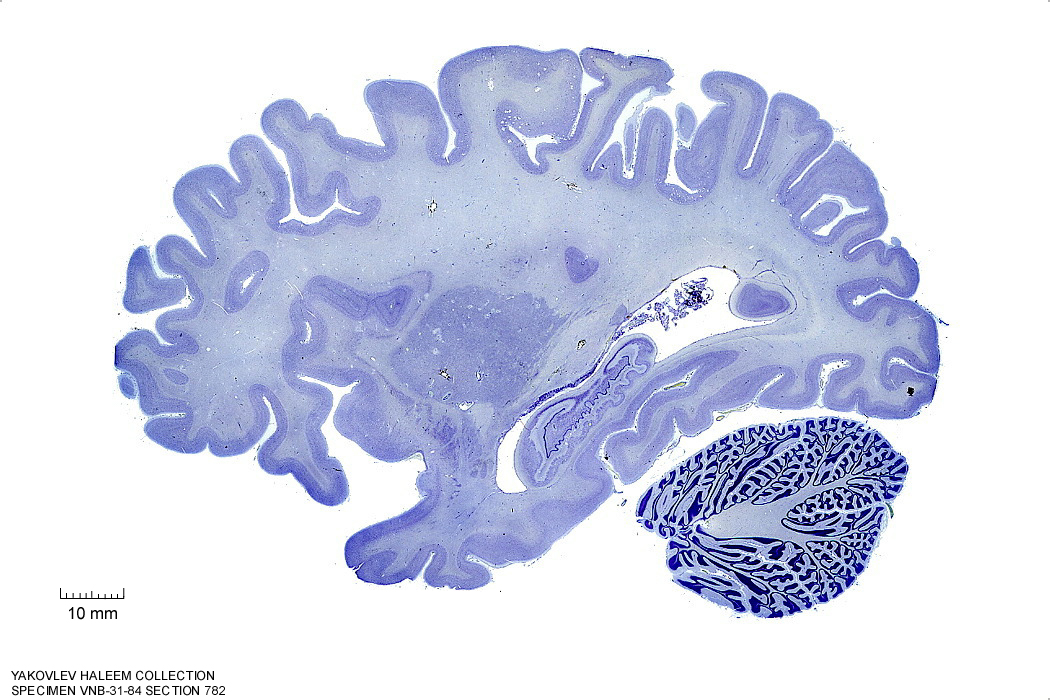
Figure 4.18: Sagittal section from The Human Brain Atlas at the Michigan State University Brain Biodiveristy Bank which acknowledges their support from the National Science Foundation.
In Figure 4.19, label the following structures:
- The external capsule
- The internal capsule
- The claustrum
- The putamen
- The anterior commissure
- The amygdala
- The optic tract
- The lateral geniculate nucleus
- The tail of the caudate nucleus
- The hippocampus
- The dentate gyrus
- The cerebellum
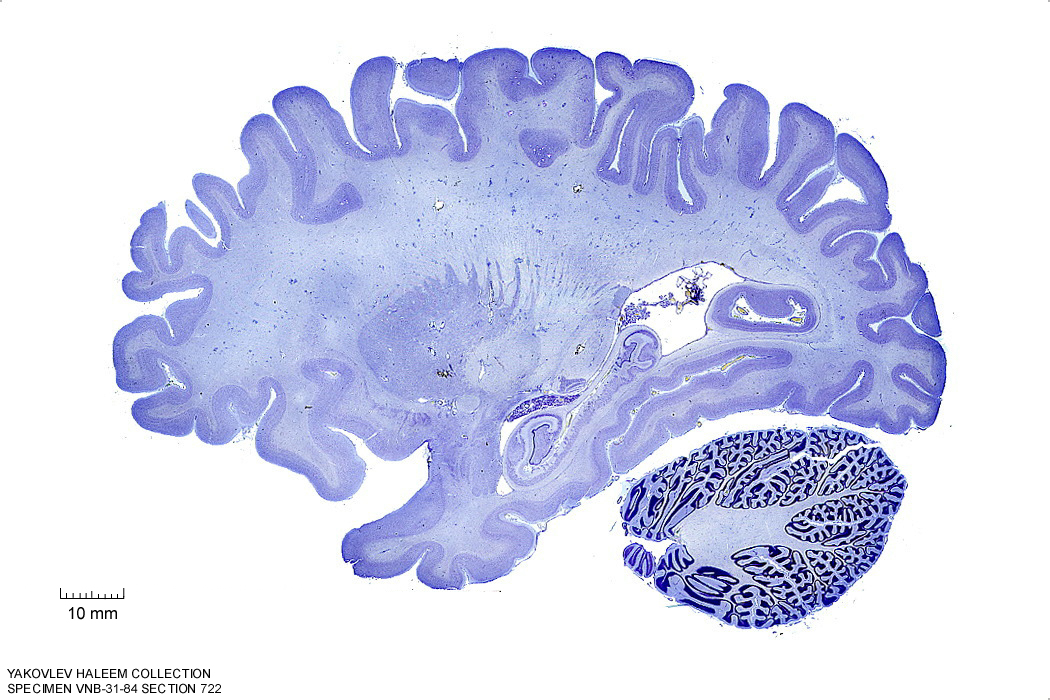
Figure 4.19: Sagittal section from The Human Brain Atlas at the Michigan State University Brain Biodiveristy Bank which acknowledges their support from the National Science Foundation.
In Figure 4.20, label the following structures:
- The thalamic nuclei
- pulvinar
- ventral group
- medial geniculate nucleus
- The internal capsule
- The claustrum
- The putamen
- The anterior commissure
- The amygdala
- The optic tract
- The lateral geniculate nucleus
- The ventral pallidum
- The cerebral peduncle
- The superior temporal gyrus
- The caudate nucleus
- The hippocampus
- The middle cerebellar peduncle
- The cerebellum
- The brachium of the superior colliculus
- The corpus callosum
- The fornix
- The superior frontal gyrus
- The lateral ventricle
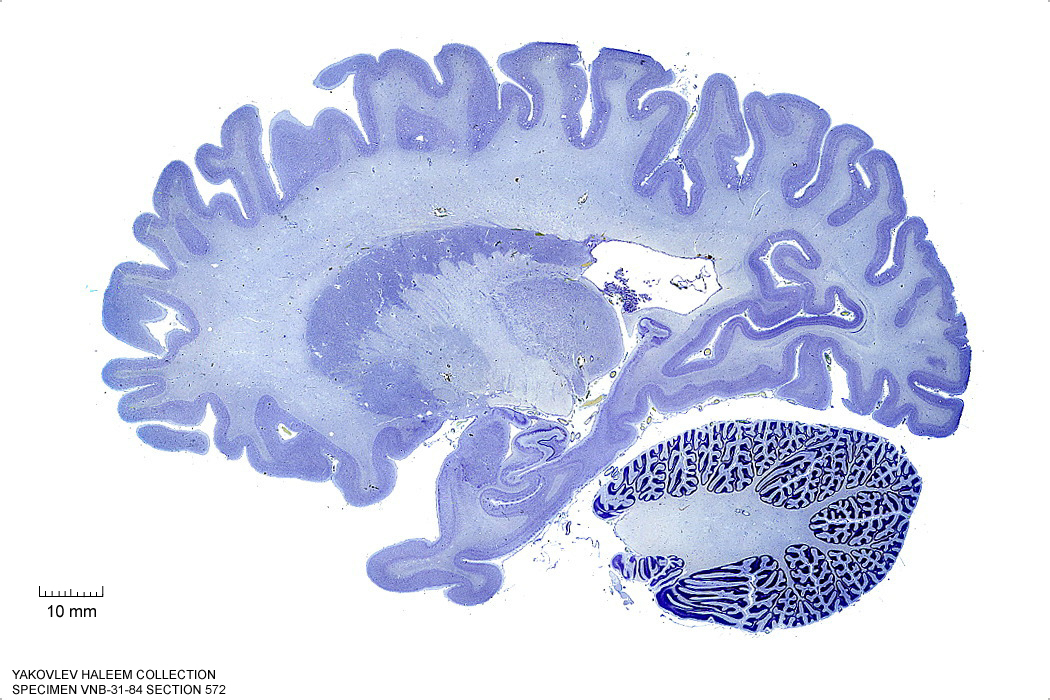
Figure 4.20: (ref:s572)
In Figure 4.21, label the following structures:
- The thalamic nuclei
- pulvinar
- ventral group
- medial geniculate nucleus
- The internal capsule
- The globus pallidus
- The ventral striatum
- The anterior commissure
- The amygdala
- The optic tract
- The lateral geniculate nucleus
- The ventral pallidum
- The cerebral peduncle
- The superior temporal gyrus
- The caudate nucleus
- The hippocampus
- The middle cerebellar peduncle
- The cerebellum
- The parieto-occipital sulcus
- The brachium of the superior colliculus
- The corpus callosum
- The fornix
- The superior frontal gyrus
- The lateral ventricle
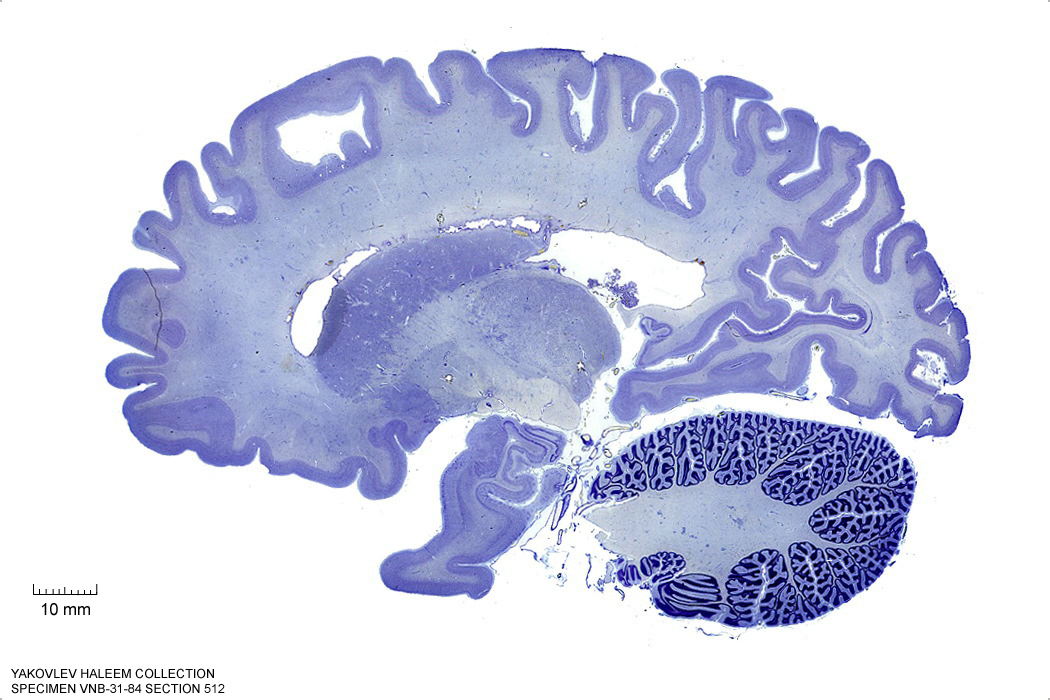
Figure 4.21: Sagittal section from The Human Brain Atlas at the Michigan State University Brain Biodiveristy Bank which acknowledges their support from the National Science Foundation.
In Figure 4.22, label the following structures:
- The superior frontal gyrus
- The thalamic nuclei
- pulvinar
- The globus pallidus
- The ventral striatum
- The anterior commissure
- The medial geniculate nucleus
- The optic tract
- The lateral geniculate nucleus
- The ventral pallidum
- The middle cerebellar peduncle
- The substantia nigra
- The cerebral peduncle
- The subthalamic nucleus
- The cerebellum
- The parieto-occipital sulcus
- The brachium of the superior colliculus
- The corpus callosum
- The fornix
- The lateral ventricle
- The dentate nucleus
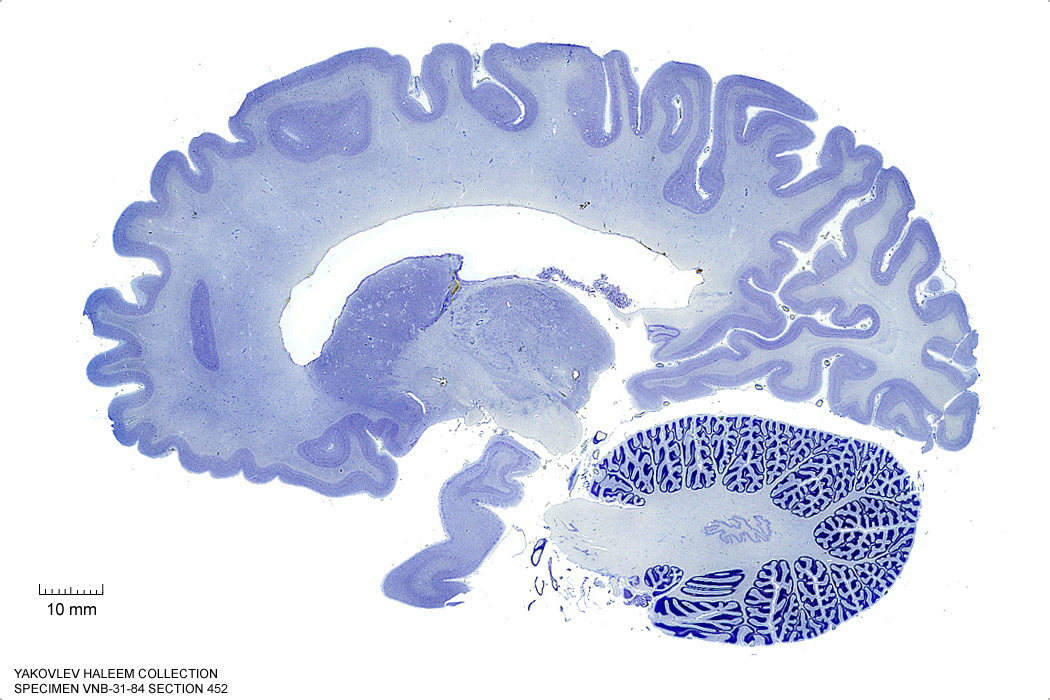
Figure 4.22: Sagittal section from The Human Brain Atlas at the Michigan State University Brain Biodiveristy Bank which acknowledges their support from the National Science Foundation.
In Figure 4.23, label the following structures:
- The corpus callosum
- the splenium
- the body
- The thalamic nuclei
- pulvinar
- ventral group
- centromedian gropup
- The anterior commissure
- The optic tract
- The caudate nucleus
- The middle cerebellar peduncle
- The cerebellum
- The fornix
- The superior frontal gyrus
- The lateral ventricle
- The parieto-occipital sulcus
- The brachium of the superior colliculus
- The brachium of the inferior colliculus
- The dentate nucleus
- The subthalamic nucleus
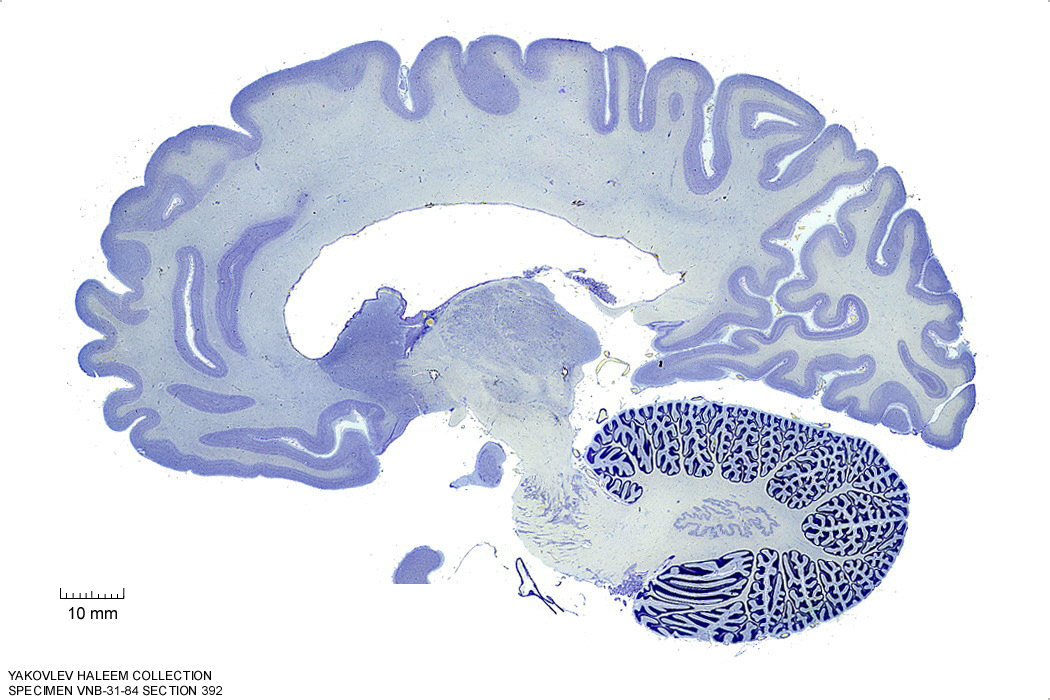
Figure 4.23: Sagittal section from The Human Brain Atlas at the Michigan State University Brain Biodiveristy Bank which acknowledges their support from the National Science Foundation.
In Figure 4.24, label the following structures:
- The corpus callosum
- the splenium
- the body
- The thalamic nuclei
- anterior group
- ventral group
- centromedian gropup
- The anterior commissure
- The hypothalamus
- The red nucleus
- The substantia nigra
- The cerebral peduncle
- The superior colliculus
- The pontine nuclei
- The optic tract
- The caudate nucleus
- The middle cerebellar peduncle
- The cerebellum
- The fornix
- The precuneus
- The cuneus
- The fornix
- The lateral ventricle
- The parieto-occipital sulcus
- The dentate nucleus
- The cerebellum
- The inferior cerebellar peduncle
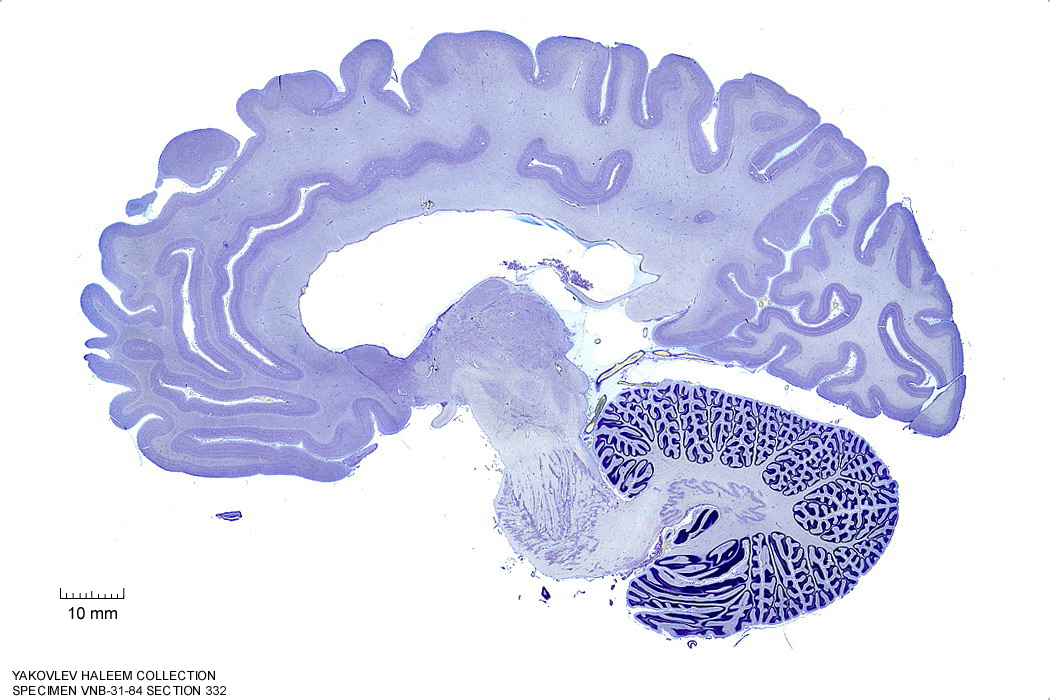
Figure 4.24: Sagittal section from The Human Brain Atlas at the Michigan State University Brain Biodiveristy Bank which acknowledges their support from the National Science Foundation.
In Figure 4.25, label the following structures:
- The corpus callosum
- the splenium
- the body
- the genu
- The thalamus
- The anterior commissure
- The mammillothalamic tract
- The hypothalamus
- The red nucleus
- The substantia nigra
- The cerebral peduncle
- The superior colliculus
- The inferior colliculus
- The lateral lemniscus
- The pontine nuclei
- The inferior cerebellar peduncle
- The cerebellum
- The fornix
- The precuneus
- The cuneus
- The fornix
- The lateral ventricle
- The parieto-occipital sulcus
- The dentate nucleus
- The lingual gyrus
- The calcarine sulcus
- The cingulate sulcus
- The cingulate gyrus
- The cerebellum
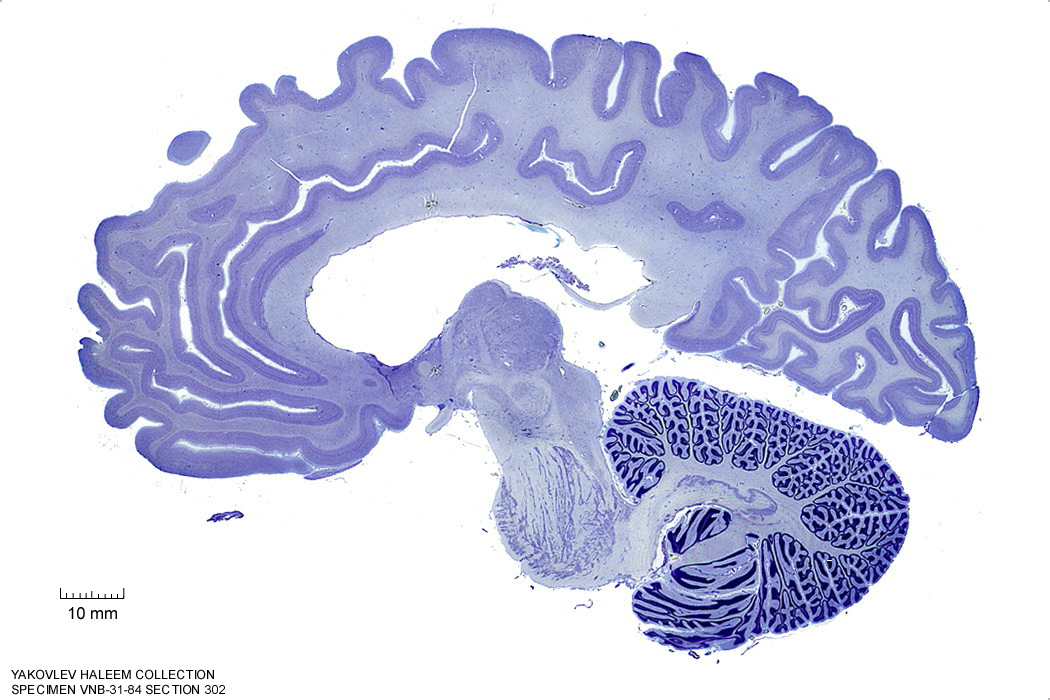
Figure 4.25: Sagittal section from The Human Brain Atlas at the Michigan State University Brain Biodiveristy Bank which acknowledges their support from the National Science Foundation.
In Figure 4.26, label the following structures:
- The superior frontal gyrus
- The corpus callosum
- the splenium
- the body
- the genu
- The thalamus
- The anterior commissure
- The mammillothalamic tract
- The hypothalamus
- The red nucleus
- The substantia nigra
- The cerebral peduncle
- The superior colliculus
- The inferior colliculus
- The lateral lemniscus
- The pontine nuclei
- The superior cerebellar peduncle
- The inferior cerebellar peduncle
- The cerebellum
- The fornix
- The precuneus
- The cuneus
- The fornix
- The lateral ventricle
- The parieto-occipital sulcus
- The dentate nucleus
- The lingual gyrus
- The calcarine sulcus
- The cingulate sulcus
- The cingulate gyrus
- The cerebellum
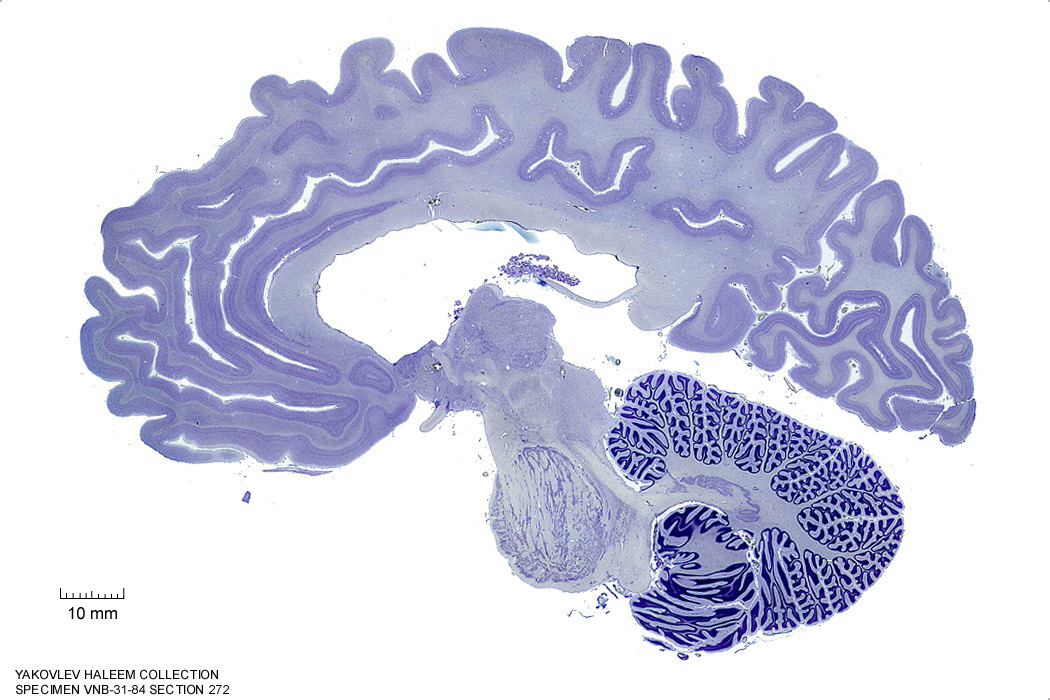
Figure 4.26: Sagittal section from The Human Brain Atlas at the Michigan State University Brain Biodiveristy Bank which acknowledges their support from the National Science Foundation.
In Figure 4.27, label the following structures:
- The superior frontal gyrus
- The corpus callosum
- the splenium
- the body
- the genu
- The thalamus
- The anterior commissure
- The mammillothalamic tract
- The hypothalamus
- The red nucleus
- The substantia nigra
- The cerebral peduncle
- The superior colliculus
- The inferior colliculus
- The lateral lemniscus
- The pontine nuclei
- The inferior olive
- The cerebellar tonsil
- The superior cerebellar peduncle
- The inferior cerebellar peduncle
- The cerebellum
- The fornix
- The precuneus
- The cuneus
- The fornix
- The lateral ventricle
- The parieto-occipital sulcus
- The lingual gyrus
- The calcarine sulcus
- The cingulate sulcus
- The cingulate gyrus
- The cerebellum
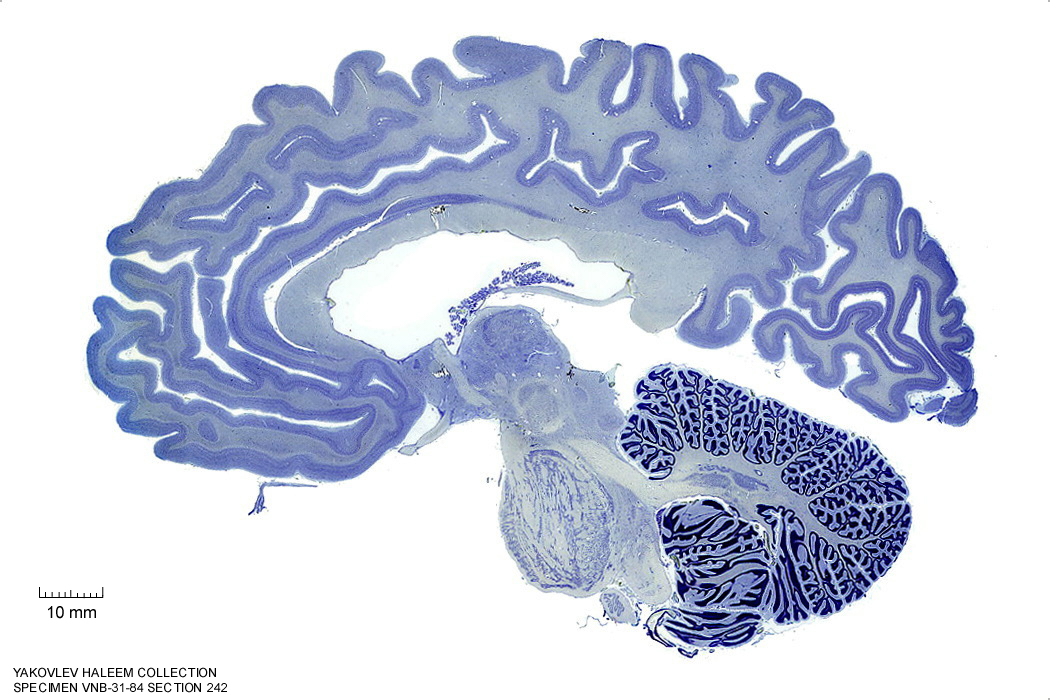
Figure 4.27: Sagittal section from The Human Brain Atlas at the Michigan State University Brain Biodiveristy Bank which acknowledges their support from the National Science Foundation.
In Figure 4.28, label the following structures:
- The corpus callosum
- the splenium
- the body
- the genu
- The thalamus
- The anterior commissure
- The mammillothalamic tract
- The hypothalamus
- The red nucleus
- The cerebral peduncle
- The superior colliculus
- The inferior colliculus
- The pontine nuclei
- The inferior olive
- The cerebellar tonsil
- The superior cerebellar peduncle
- The cerebellum
- The fornix
- The precuneus
- The cuneus
- The fornix
- The lateral ventricle
- The parieto-occipital sulcus
- The lingual gyrus
- The calcarine sulcus
- The cingulate sulcus
- The cingulate gyrus
- The cerebellum
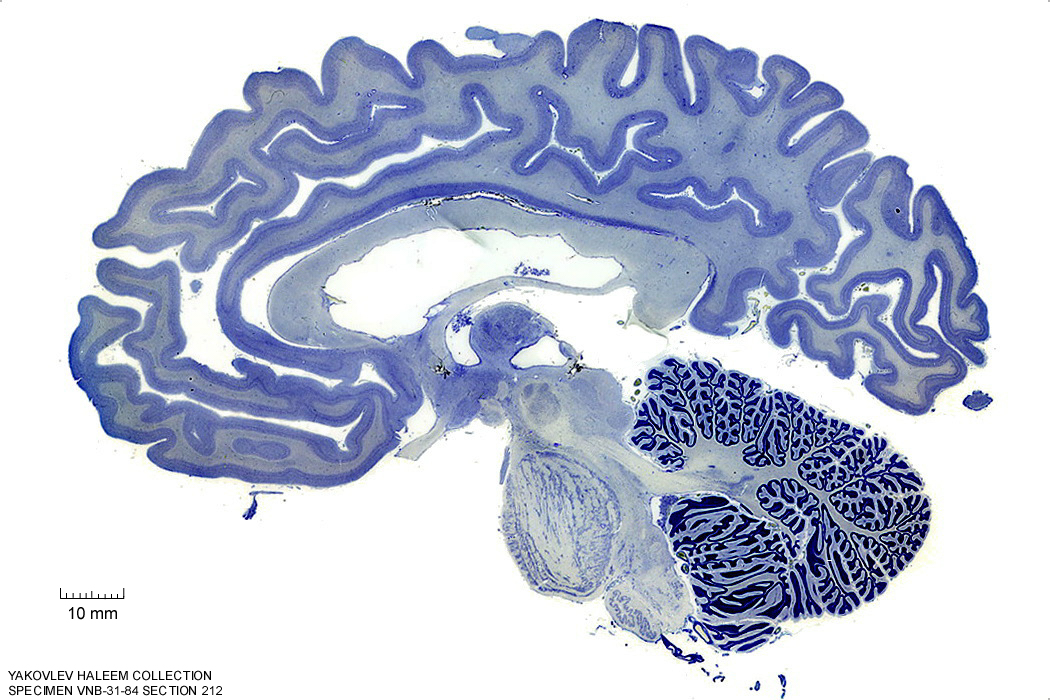
Figure 4.28: Sagittal section from The Human Brain Atlas at the Michigan State University Brain Biodiveristy Bank which acknowledges their support from the National Science Foundation.
In Figure 4.29, label the following structures:
- The corpus callosum
- the splenium
- the body
- the genu
- The thalamus
- The anterior commissure
- The optic chiasm
- The lamina terminalis
- The mammillothalamic tract
- The mammillariy nuclei
- The hypothalamus
- The red nucleus
- The cerebral peduncle
- The superior colliculus
- The inferior colliculus
- The pontine nuclei
- The inferior olive
- The cerebellar tonsil
- The decussation of the superior cerebellar peduncle
- The cerebellum
- The fornix
- The habenular commissure
- The septum lucidum
- The periaqueductal grey matter
- The precuneus
- The cuneus
- The fornix
- The lateral ventricle
- The parieto-occipital sulcus
- The lingual gyrus
- The calcarine sulcus
- The cingulate sulcus
- The cingulate gyrus
- The cerebellum
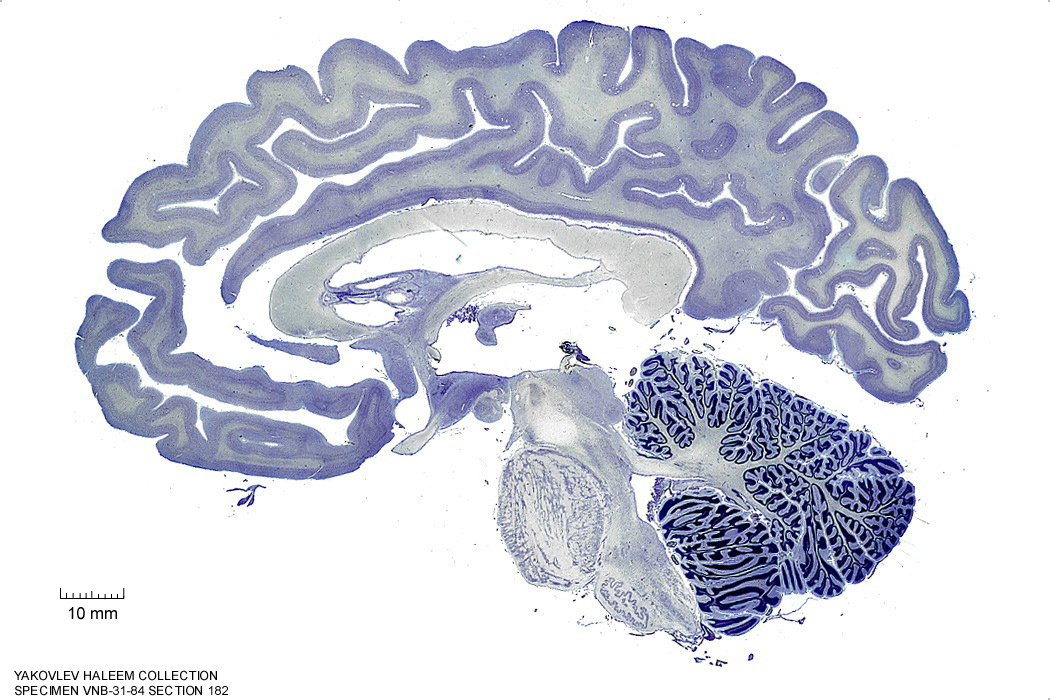
Figure 4.29: Sagittal section from The Human Brain Atlas at the Michigan State University Brain Biodiveristy Bank which acknowledges their support from the National Science Foundation.
In Figure 4.30, label the following structures:
- The corpus callosum
- the splenium
- the body
- the genu
- The thalamus
- The anterior commissure
- The optic chiasm
- The lamina terminalis
- The mammillothalamic tract
- The mammillariy nuclei
- The hypothalamus
- The red nucleus
- The cerebral peduncle
- The superior colliculus
- The inferior colliculus
- The pontine nuclei
- The inferior olive
- The cerebellar tonsil
- The decussation of the superior cerebellar peduncle
- The cerebellum
- The fornix
- The habenular commissure
- The septum lucidum
- The periaqueductal grey matter
- The precuneus
- The cuneus
- The fornix
- The lateral ventricle
- The parieto-occipital sulcus
- The gracile nucleus
- The cuneate fasciculus
- The 4th ventricle
- The lingual gyrus
- The calcarine sulcus
- The cingulate sulcus
- The cingulate gyrus
- The cerebellum
- The cerebral aqueduct
- The posterior commissure

Figure 4.30: Sagittal section from The Human Brain Atlas at the Michigan State University Brain Biodiveristy Bank which acknowledges their support from the National Science Foundation.
4.3 A Series Of Horizontal Sections Of A Human Brain
In Figure 4.31, label the following structures:
- The middle frontal gyrus
- The superior frontal gyrus
- The superior frontal sulcus
- The medial longitudinal fissure
- The precuneus
- The cingulate gyrus
- The precentral sulcus
- The precentral gyrus
- The central sulcus
- The postcentral gyrus
- The postcentral sulcus
- The supramarginal gyrus
- The intraparietal sulcus
- The superior parietal lobule
- The parieto-occipital sulcus
- The intraparietal sulcus
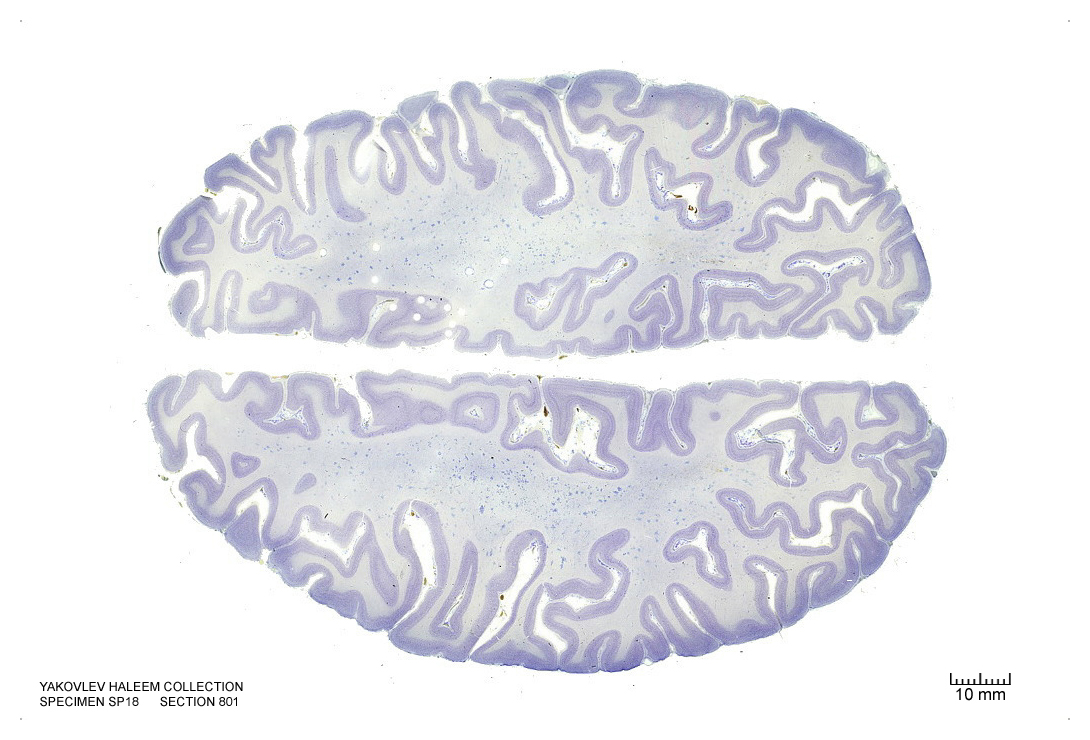
Figure 4.31: Horizontal section from The Human Brain Atlas at the Michigan State University Brain Biodiveristy Bank which acknowledges their support from the National Science Foundation.
In Figure 4.32, label the following structures:
- The middle frontal gyrus
- The inferior frontal gyrus
- The inferior frontal sulcus
- The medial longitudinal fissure
- The precuneus
- The cingulate gyrus
- The cingulate sulcus
- The superior frontal gyrus
- The superior frontal sulcus
- The angular gyrus
- The precentral sulcus
- The precentral gyrus
- The central sulcus
- The postcentral gyrus
- The postcentral sulcus
- The supramarginal gyrus
- The intraparietal sulcus
- The superior parietal lobule
- The parieto-occipital sulcus
- The intraparietal sulcus
- The lateral sulcus
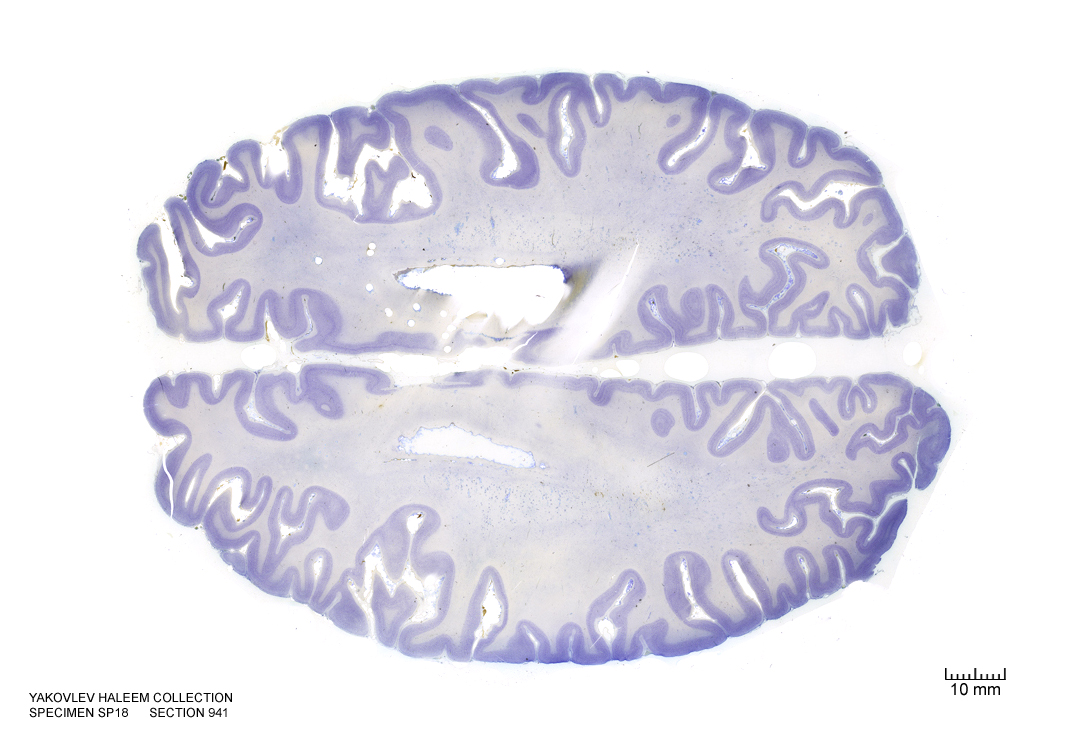
Figure 4.32: Horizontal section from The Human Brain Atlas at the Michigan State University Brain Biodiveristy Bank which acknowledges their support from the National Science Foundation.
In Figure 4.33, label the following structures:
- The middle frontal gyrus
- The inferior frontal gyrus
- The inferior frontal sulcus
- The medial longitudinal fissure
- The precuneus
- The cuneus
- The cingulate gyrus
- The cingulate sulcus
- The superior frontal gyrus
- The superior frontal sulcus
- The angular gyrus
- The precentral sulcus
- The precentral gyrus
- The central sulcus
- The postcentral gyrus
- The postcentral sulcus
- The supramarginal gyrus
- The intraparietal sulcus
- The superior parietal lobule
- The parieto-occipital sulcus
- The intraparietal sulcus
- the lateral sulcus
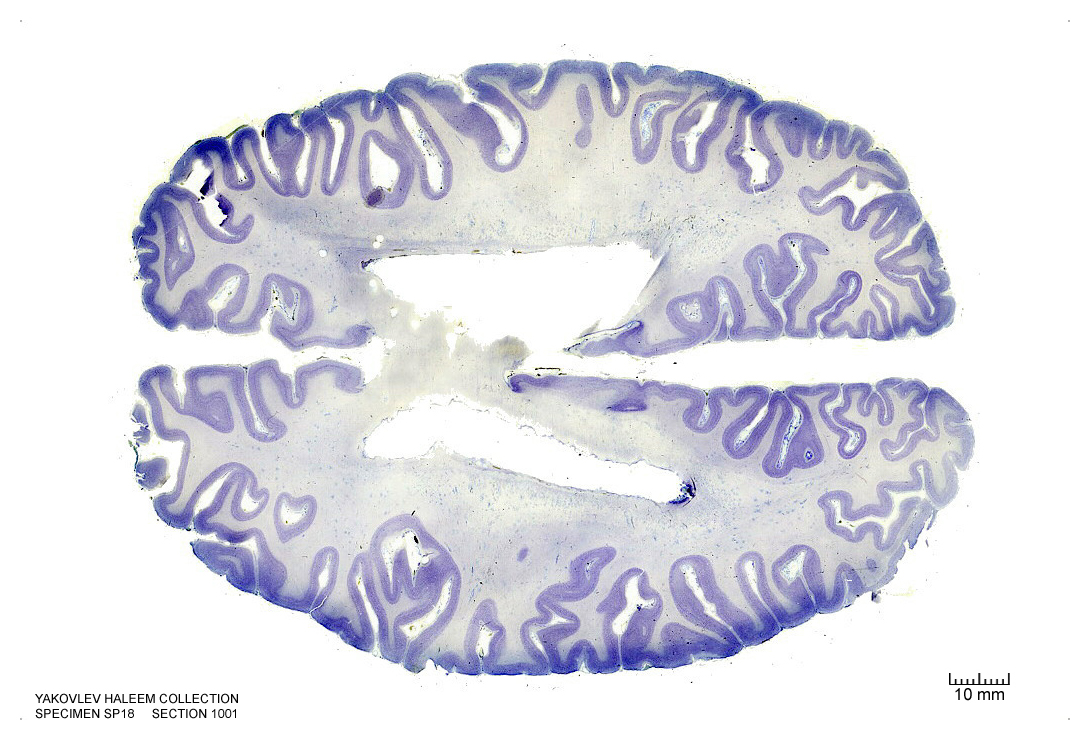
Figure 4.33: Horizontal section from The Human Brain Atlas at the Michigan State University Brain Biodiveristy Bank which acknowledges their support from the National Science Foundation.
In Figure 4.34, label the following structures:
- The middle frontal gyrus
- The inferior frontal gyrus
- The inferior frontal sulcus
- The medial longitudinal fissure
- The precuneus
- The cuneus
- The cingulate gyrus
- The cingulate sulcus
- The callosal sulcus
- The lateral ventricle
- The septum pellucidum
- The insula
- The corpus callosum
- The superior frontal gyrus
- The superior frontal sulcus
- The angular gyrus
- The precentral sulcus
- The precentral gyrus
- The central sulcus
- The postcentral gyrus
- The postcentral sulcus
- The supramarginal gyrus
- The intraparietal sulcus
- The superior parietal lobule
- The parieto-occipital sulcus
- The intraparietal sulcus
- the lateral sulcus
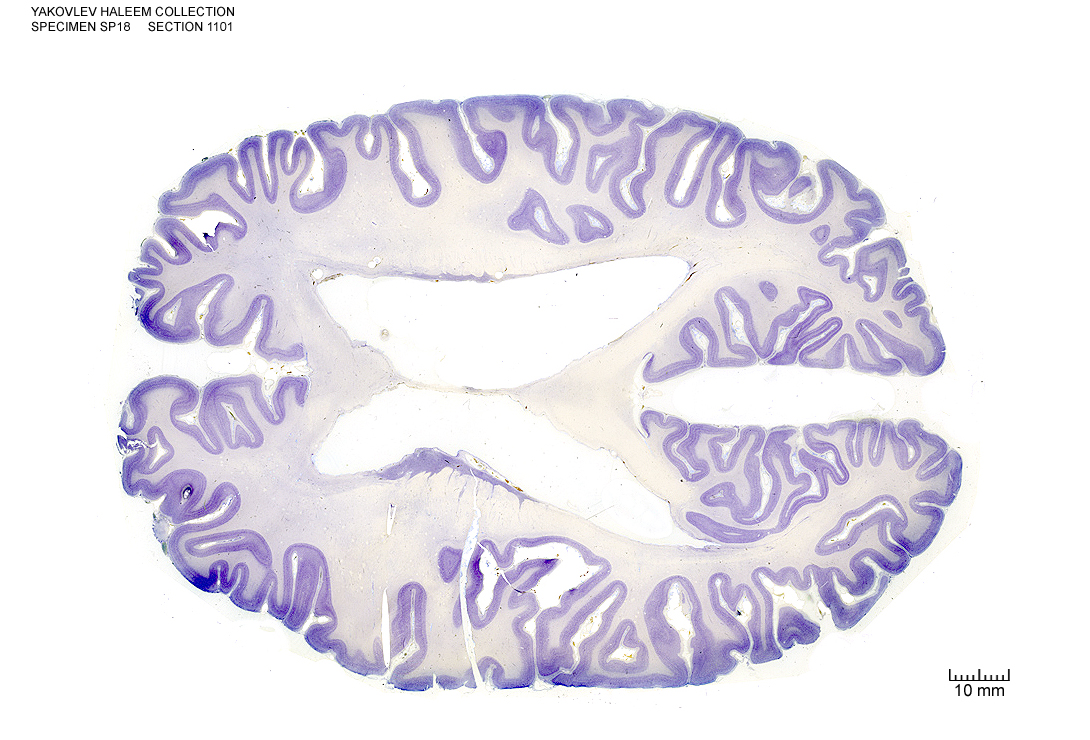
Figure 4.34: (ref:h11100)
In Figure 4.35, label the following structures:
- The sulcus of the corpus callosum
- The splenium of the corpus callosum
- The lateral ventricle
- The septum pellucidum
- The insular cortex
- The head of the caudate nucleus
- The body of the caudate nucleus
- The external capsule
- The putamen
- The tail of the caudate nucleus
- The occipital horn of the lateral ventricle
- The fornix
- The medial longitudinal fissure
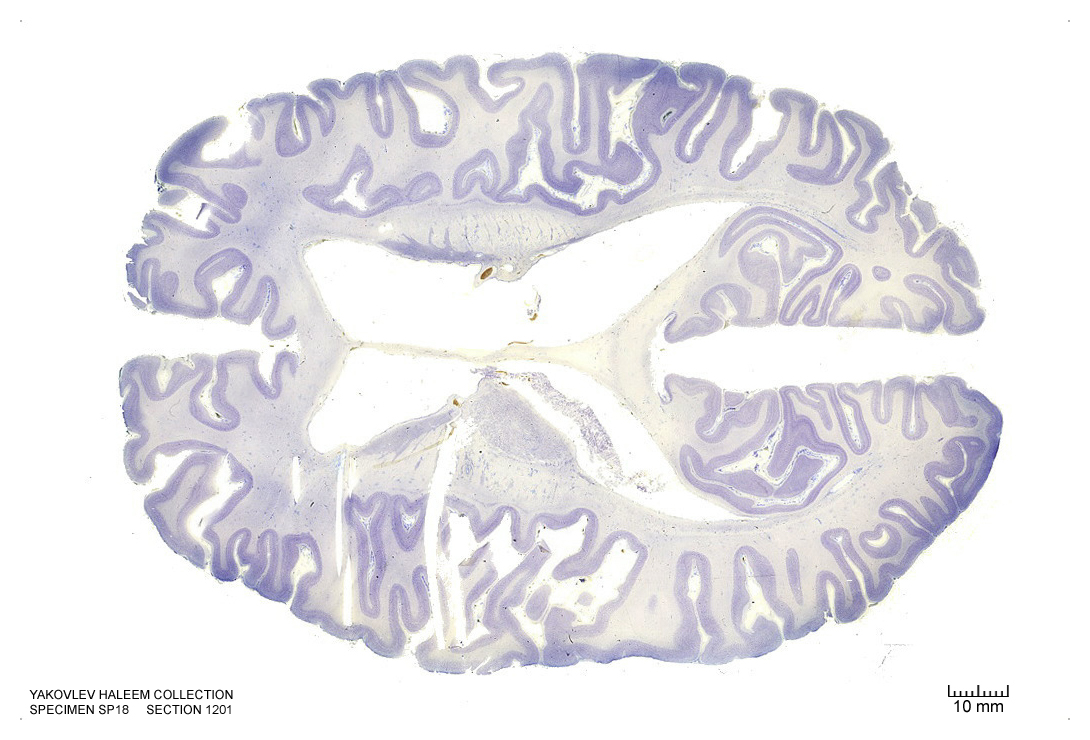
Figure 4.35: Horizontal section from The Human Brain Atlas at the Michigan State University Brain Biodiveristy Bank which acknowledges their support from the National Science Foundation.
In Figure 4.36, label the following structures:
- The thalamic nuclei
- reticular
- ventroposterior
- ventroanterior
- ventrolateral
- mediodorsal
- anteroprincipal
- The lateral ventricle
- The choroid plexus
- The splenium of the corpus callosum
- The lateral ventricle
- The septum pellucidum
- The insular cortex
- The head of the caudate nucleus
- The body of the caudate nucleus
- The tail of the caudate nucleus
- The external capsule
- The putamen
- The occipital horn of the lateral ventricle
- The fornix
- The medial longitudinal fissure
- The vermis of the cerebellum
- The dentate gyrus
- The internal capsule
- The subiculum
- The primary visual cortex
- The calcarine sulcus
- The fornix
- The cingulate sulcus
- The cingulate gyrus
- The genu of the corpus callosum
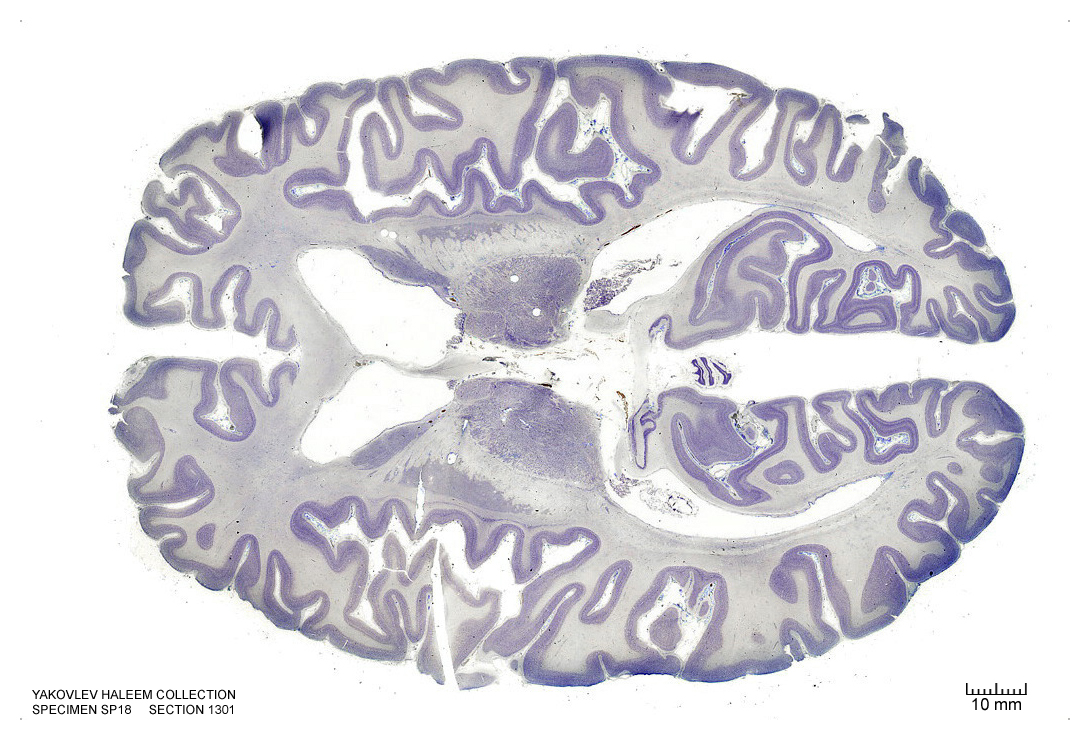
Figure 4.36: Horizontal section from The Human Brain Atlas at the Michigan State University Brain Biodiveristy Bank which acknowledges their support from the National Science Foundation.
In Figure 4.37, label the following structures:
- The thalamic nuclei
- pulvinar
- reticular
- ventroposterior
- ventroanterior
- ventrolateral
- mediodorsal
- The habenula
- The lateral ventricle
- The septum pellucidum
- The insular cortex
- The head of the caudate nucleus
- The tail of the caudate nucleus
- The external capsule
- The fornix
- The septal nuclei
- The medial longitudinal fissure
- The vermis of the cerebellum
- The dentate gyrus
- The subiculum
- The primary visual cortex
- The calcarine sulcus
- The choroid plexus
- The superior temporal gyrus
- The putamen
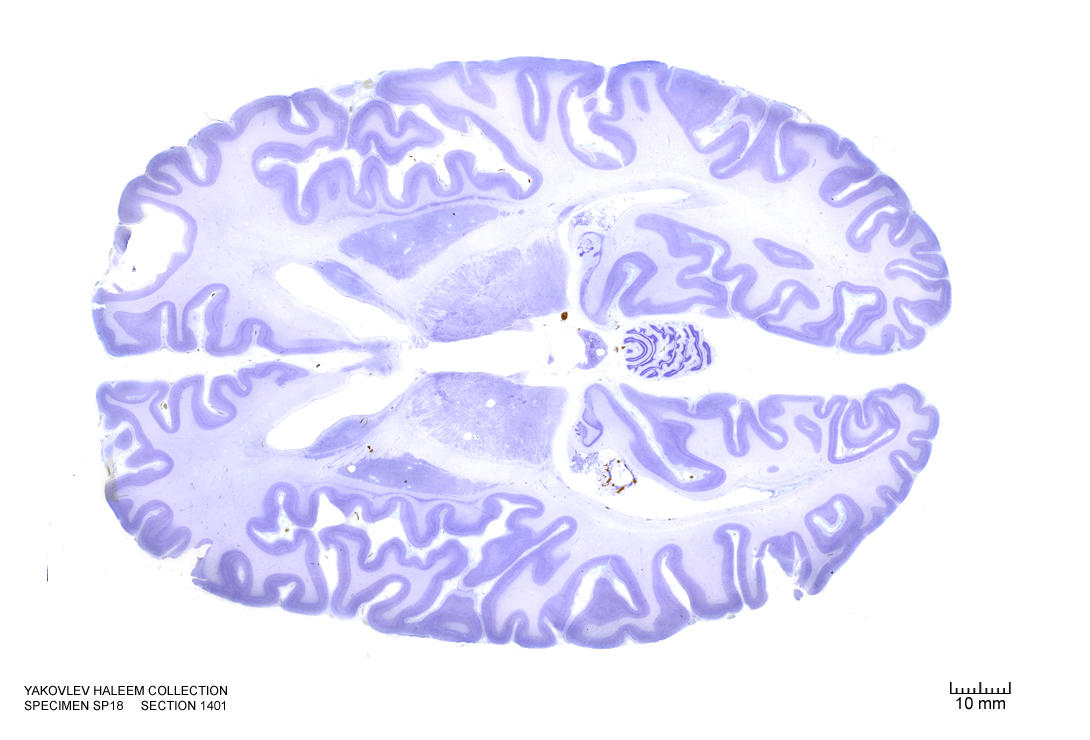
Figure 4.37: Horizontal section from The Human Brain Atlas at the Michigan State University Brain Biodiveristy Bank which acknowledges their support from the National Science Foundation.
In Figure 4.38, label the following structures:
- The thalamic nuclei
- pulvinar
- reticular
- The 3d ventricle
- The fimbria of the hippocampus
- The claustrum
- The medial geniculate nucleus
- The lateral geniculate nucleus
- The superior colliculus
- The cerebellum
- The head of the caudate nucleus
- The tail of the caudate nucleus
- The external capsule
- The fornix
- The septal nuclei
- The medial longitudinal fissure
- The cerebellum
- The dentate gyrus
- The hippocampus
- The subiculum
- The optic tract
- The insular cortex
- The primary visual cortex
- The calcarine sulcus
- The choroid plexus
- The superior temporal gyrus
- The putamen
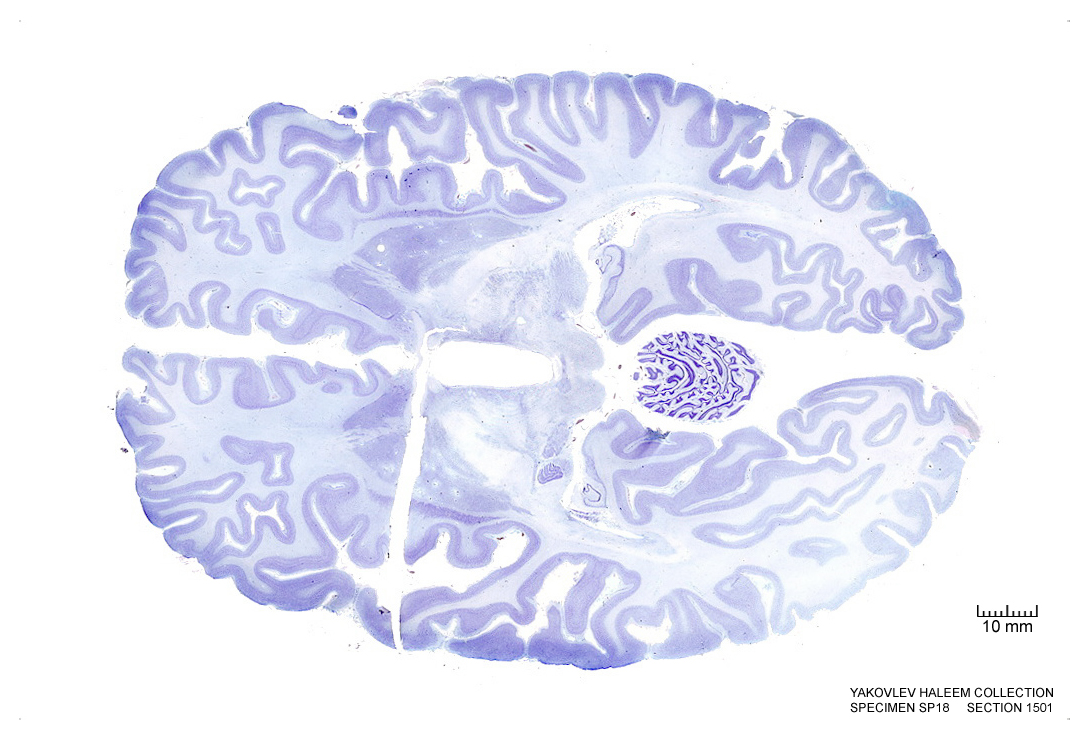
Figure 4.38: Horizontal section from The Human Brain Atlas at the Michigan State University Brain Biodiveristy Bank which acknowledges their support from the National Science Foundation.
In Figure 4.39, label the following structures:
- The cerebral aqueduct
- The mammillothalamic tract
- The red nucleus
- The choroid plexus
- The cerebral peduncle
- The fimbria of the hippocampus
- The medial geniculate nucleus
- The lateral geniculate nucleus
- The inferior colliculus
- The cerebellum
- The vermis of the cerebellum
- The external capsule
- The claustrum
- The ventral striatum
- The medial longitudinal fissure
- The vermis of the cerebellum
- The dentate gyrus
- The hippocampus
- The subiculum
- The optic tract
- The insular cortex
- The primary visual cortex
- The calcarine sulcus
- The substantia nigra
- The fornix
- The optic tract
- The external capsule
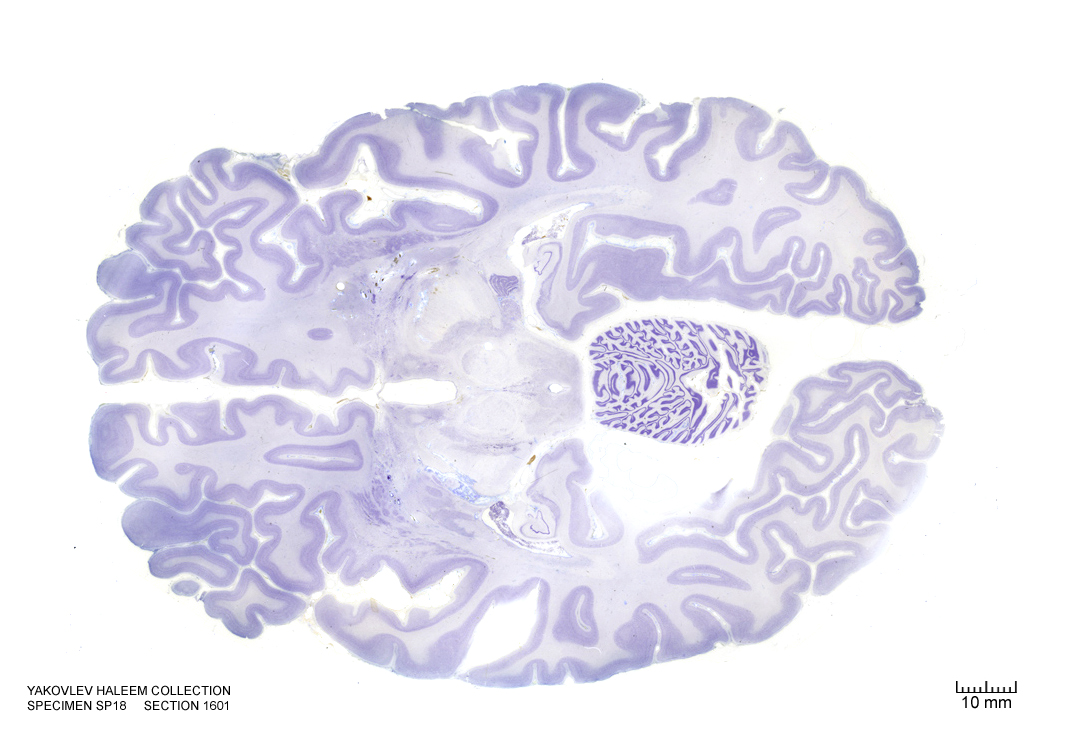
Figure 4.39: Horizontal section from The Human Brain Atlas at the Michigan State University Brain Biodiveristy Bank which acknowledges their support from the National Science Foundation.
In Figure 4.40, label the following structures:
- The cerebral aqueduct
- The red nucleus
- The choroid plexus
- The cerebral peduncle
- The dorsal raphe nucleus
- The periaqueductal grey area
- The 3d ventricle
- The fimbria of the hippocampus
- The medial geniculate nucleus
- The lateral geniculate nucleus
- The inferior colliculus
- The cerebellum
- The vermis of the cerebellum
- The external capsule
- The claustrum
- The ventral striatum
- The medial longitudinal fissure
- The vermis of the cerebellum
- The dentate gyrus
- The hippocampus
- The subiculum
- The optic tract
- The insular cortex
- The primary visual cortex
- The substantia nigra
- The medial lemniscus
- The amygdala
- The orbital gyri
- The ventromedial hypothalamic nucleus
- The ventral striatum
- The fornix
- The optic tract
- The external capsule
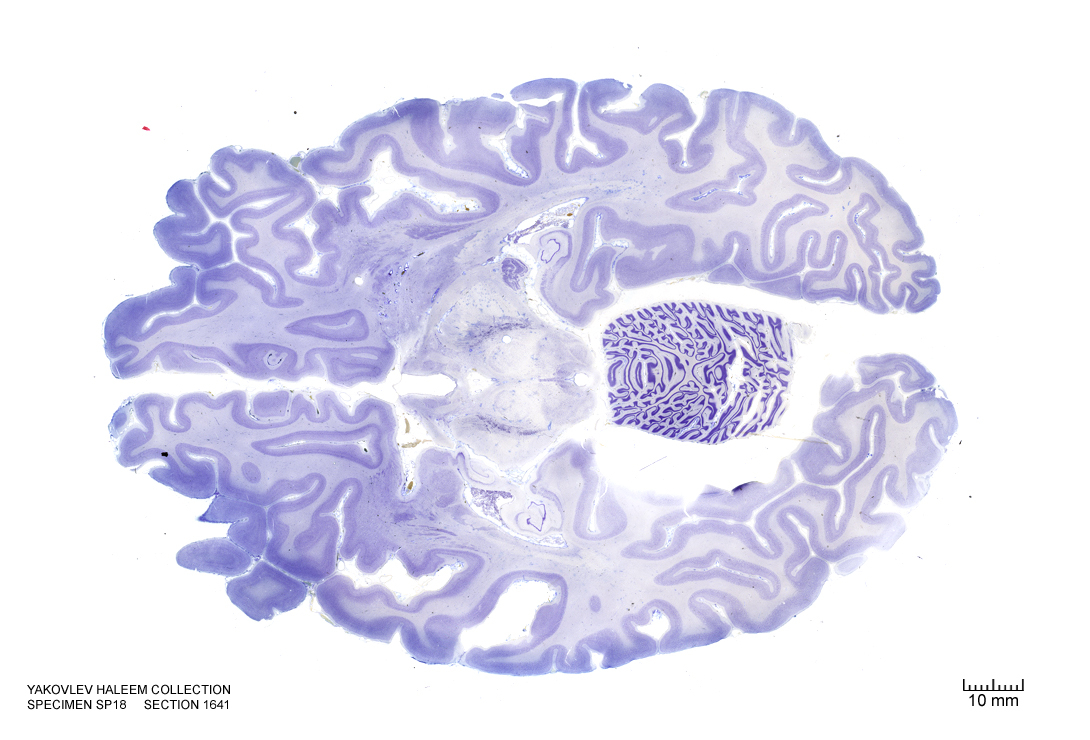
Figure 4.40: Horizontal section from The Human Brain Atlas at the Michigan State University Brain Biodiveristy Bank which acknowledges their support from the National Science Foundation.
In Figure 4.41, label the following structures:
- The cerebral aqueduct
- The red nucleus
- The choroid plexus
- The cerebral peduncle
- The dorsal raphe nucleus
- The periaqueductal grey area
- The 3d ventricle
- The fimbria of the hippocampus
- The medial geniculate nucleus
- The lateral geniculate nucleus
- The inferior colliculus
- The cerebellum
- The vermis of the cerebellum
- The external capsule
- The claustrum
- The ventral striatum
- The medial longitudinal fissure
- The vermis of the cerebellum
- The dentate gyrus
- The hippocampus
- The subiculum
- The optic tract
- The insular cortex
- The primary visual cortex
- The substantia nigra
- The medial lemniscus
- The amygdala
- The orbital gyri
- The ventromedial hypothalamic nucleus
- The ventral striatum
- The fornix
- The optic tract
- The external capsule
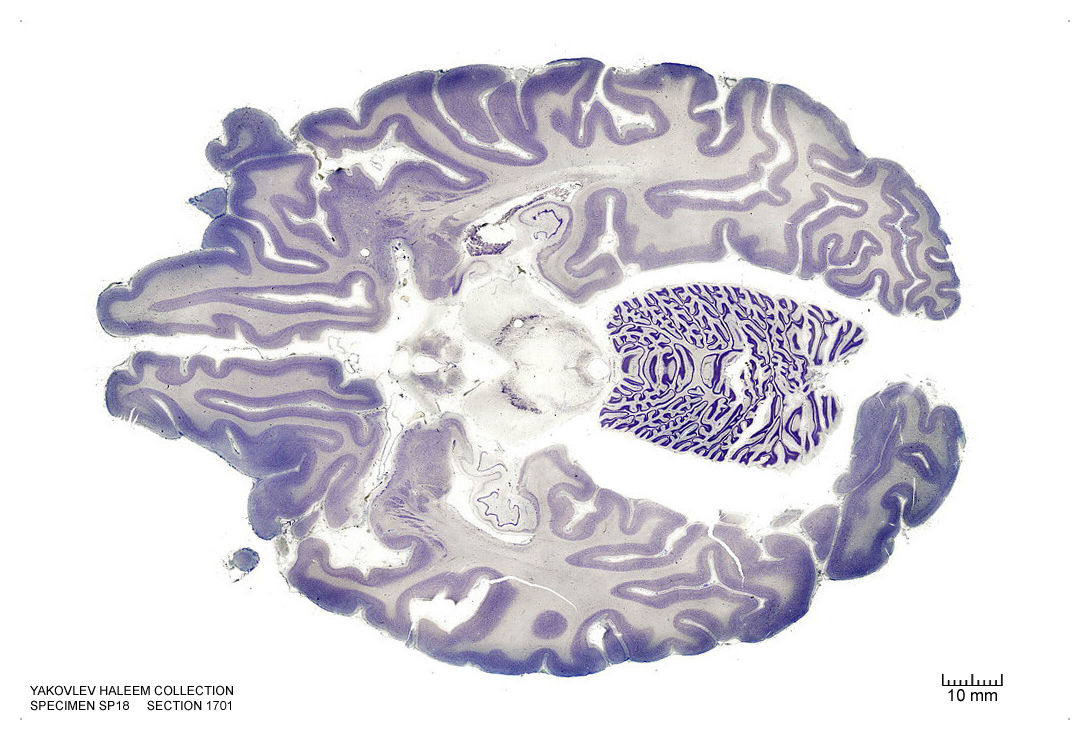
Figure 4.41: Horizontal section from The Human Brain Atlas at the Michigan State University Brain Biodiveristy Bank which acknowledges their support from the National Science Foundation.
In Figure 4.42, label the following structures:
- The cerebral aqueduct
- The arcuate hypothalamic nucleus
- The choroid plexus
- The cerebral peduncle
- The dorsal raphe nucleus
- The periaqueductal grey area
- The 3d ventricle
- The fimbria of the hippocampus
- The locus coeruleus
- The cerebellum
- The vermis of the cerebellum
- The external capsule
- The claustrum
- The medial longitudinal fissure
- The vermis of the cerebellum
- The dentate gyrus
- The hippocampus
- The subiculum
- The optic tract
- The insular cortex
- The primary visual cortex
- The substantia nigra
- The medial lemniscus
- The amygdala
- The orbital gyri
- The optic tract
- The external capsule
- The olfactory sulcus
- The interpeduncular fossa
- The decussation of the superior cerebellar peduncles
- The medial lemniscus
- The 3d ventricle
- The 4th ventricle
- The raphe nucleus
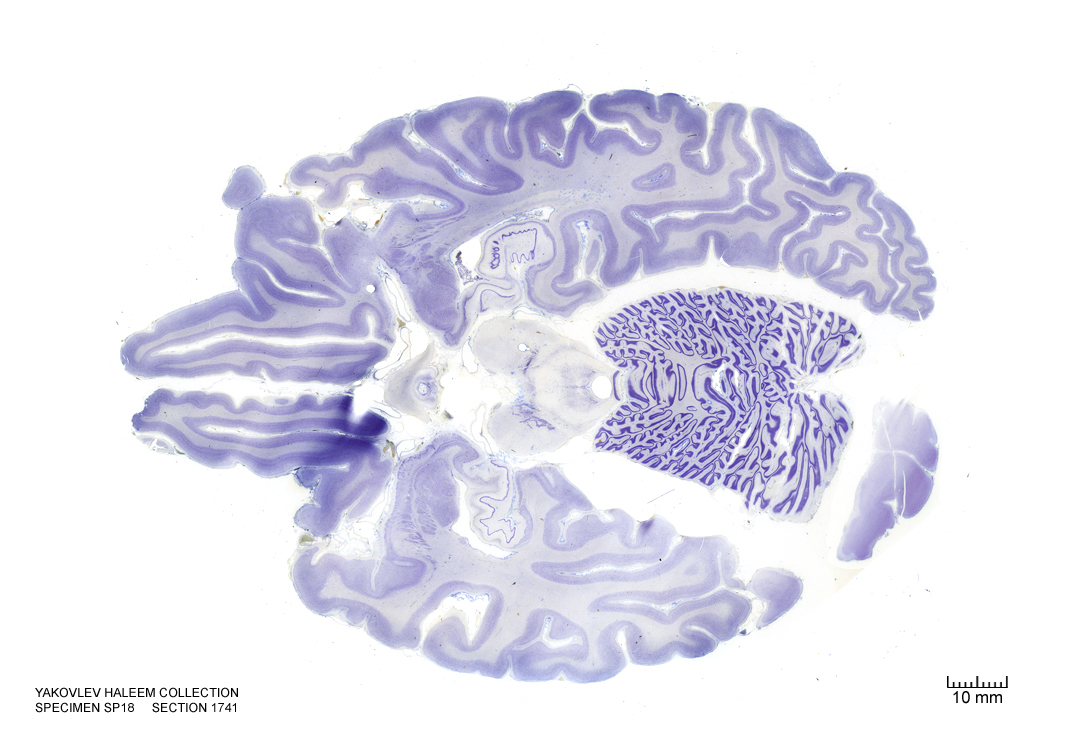
Figure 4.42: Horizontal section from The Human Brain Atlas at the Michigan State University Brain Biodiveristy Bank which acknowledges their support from the National Science Foundation.
In Figure 4.43, label the following structures:
- The arcuate hypothalamic nucleus
- The infundibular stalk
- The raphe nuclei
- The central grey of the pons
- The 3d ventricle
- The locus coeruleus
- The cerebellum
- The vermis of the cerebellum
- The external capsule
- The medial longitudinal fissure
- The vermis of the cerebellum
- The dentate gyrus
- The hippocampus
- The subiculum
- The optic nerve
- The insular cortex
- The claustrum
- The primary visual cortex
- The medial lemniscus
- The amygdala
- The medial lemniscus
- The 4th ventricle
- The trigeminal nerve
- The superior cerebellar peduncle
- The central tegmental tract
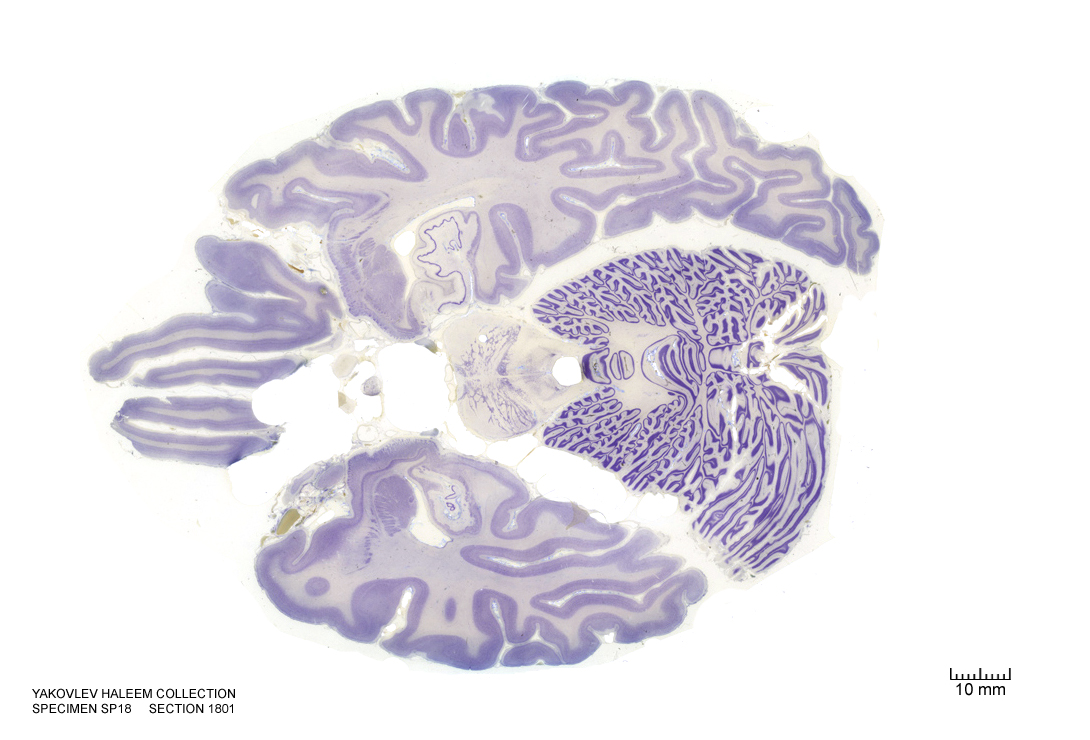
Figure 4.43: Horizontal section from The Human Brain Atlas at the Michigan State University Brain Biodiveristy Bank which acknowledges their support from the National Science Foundation.
In Figure 4.44, label the following structures:
- The raphe nuclei
- The central grey of the pons
- The 3d ventricle
- The locus coeruleus
- The cerebellum
- The vermis of the cerebellum
- The external capsule
- The medial longitudinal fissure
- The dentate gyrus
- The hippocampus
- The subiculum
- The optic nerve
- The primary visual cortex
- The amygdala
- The medial lemniscus
- The 4th ventricle
- The trigeminal nerve
- The superior cerebellar peduncle
- The central tegmental tract
- The dentate nucleus
- The emboliform nucleus
- The fastigial nucleus
- The medial lemniscus
- The entorhinal cortex
- The lateral ventricle
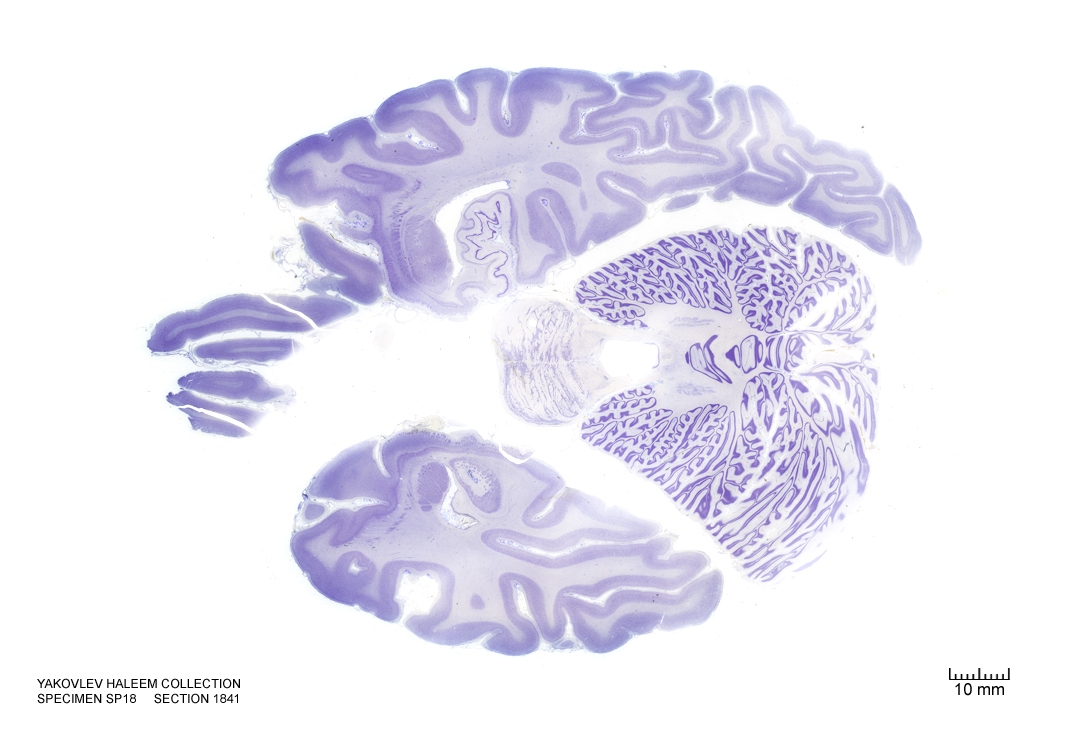
Figure 4.44: Horizontal section from The Human Brain Atlas at the Michigan State University Brain Biodiveristy Bank which acknowledges their support from the National Science Foundation.
In Figure 4.45, label the following structures:
- The raphe nuclei
- The central grey of the pons
- The 3d ventricle
- The locus coeruleus
- The cerebellum
- The vermis of the cerebellum
- The external capsule
- The medial longitudinal fissure
- The dentate gyrus
- The hippocampus
- The subiculum
- The optic nerve
- The primary visual cortex
- The amygdala
- The medial lemniscus
- The 4th ventricle
- The trigeminal nerve
- The superior cerebellar peduncle
- The dentate nucleus
- The emboliform nucleus
- The fastigial nucleus
- The medial lemniscus
- The entorhinal cortex
- The lateral ventricle
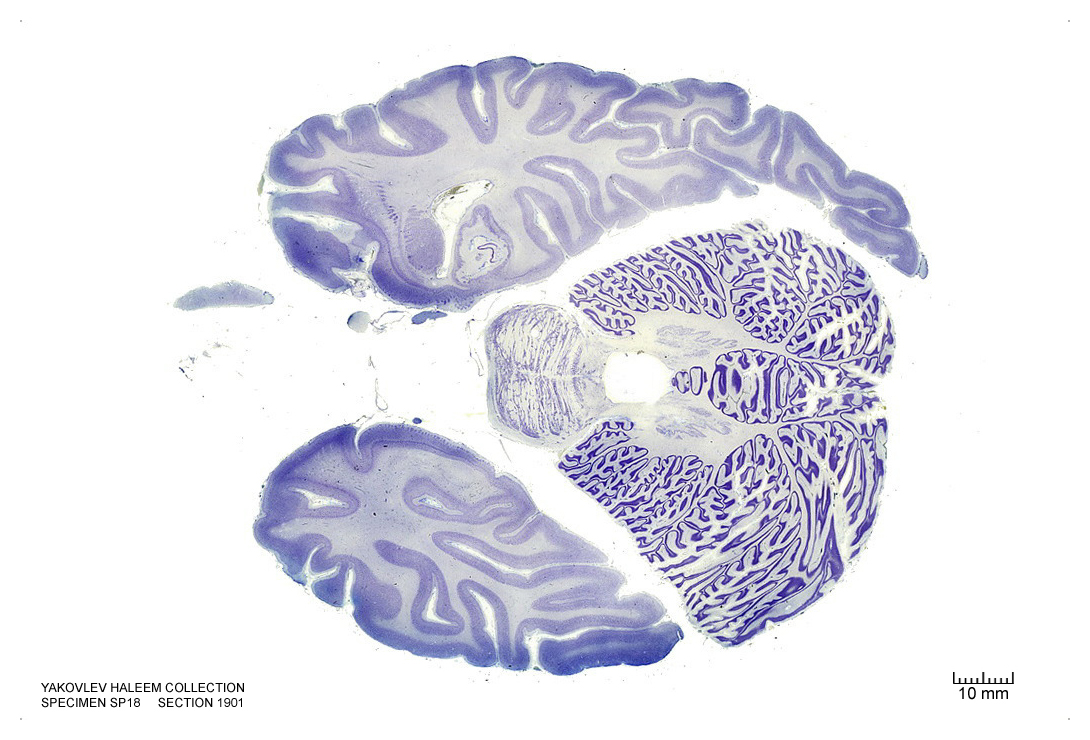
Figure 4.45: Horizontal section from The Human Brain Atlas at the Michigan State University Brain Biodiveristy Bank which acknowledges their support from the National Science Foundation.
In Figure 4.46, label the following structures:
- The solitary tract and nucleus
- The facial nucleus
- The facial nerve root
- The olivary nuclei
- The raphe nuclei
- The central grey of the pons
- The 3d ventricle
- The locus coeruleus
- The cerebellum
- The vermis of the cerebellum
- The external capsule
- The medial longitudinal fissure
- The dentate gyrus
- The hippocampus
- The subiculum
- The 4th ventricle
- The trigeminal nerve
- The superior cerebellar peduncle
- The dentate nucleus
- The entorhinal cortex
- The superior vestibular nucleus
- The spinal trigeminal nucleus
- The middle cerebellar peduncle
- The central tegmental tract
- The reticular formation
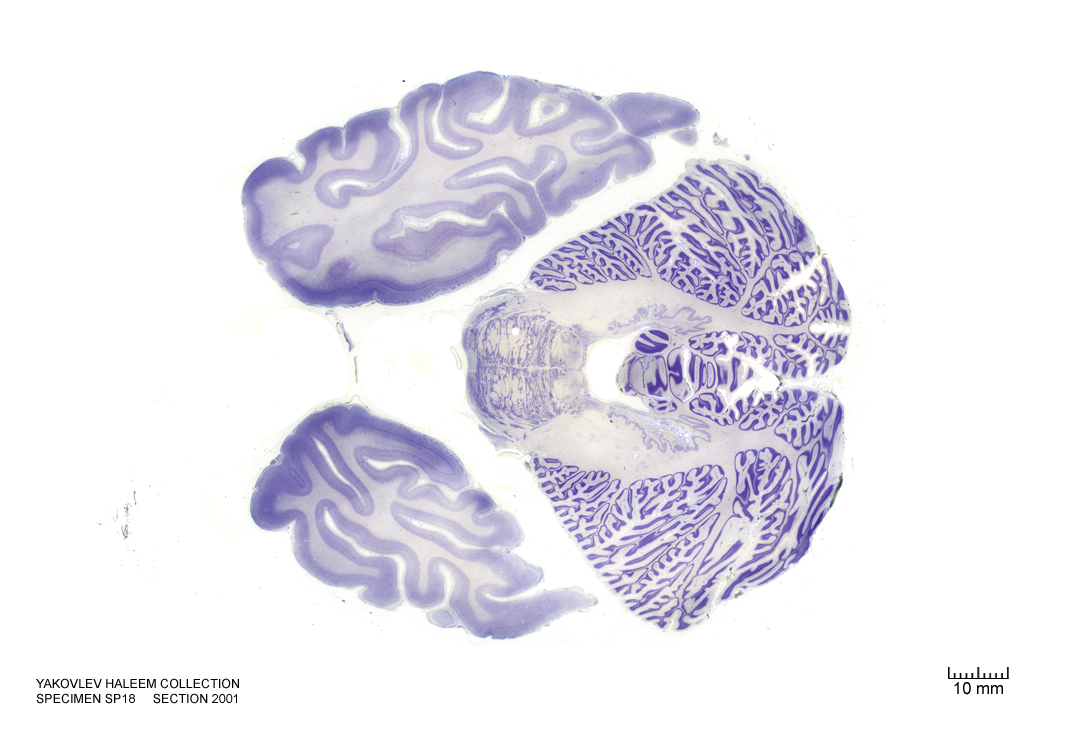
Figure 4.46: Horizontal section from The Human Brain Atlas at the Michigan State University Brain Biodiveristy Bank which acknowledges their support from the National Science Foundation.
In Figure 4.47, label the following structures:
- The solitary tract and nucleus
- The facial motor nucleus
- The corticospinal fibers
- The superior olivary nuclei
- The cerebellum
- The vermis of the cerebellum
- The dentate gyrus
- The 4th ventricle
- The trigeminal nerve
- The superior cerebellar peduncle
- The dentate nucleus
- The entorhinal cortex
- The superior vestibular nucleus
- The spinal trigeminal nucleus
- The spinal trigeminal tract
- The middle cerebellar peduncle
- The central tegmental tract
- The reticular formation
- The middle cerebellar peduncle
- The cerebellar tonsil
- The medial longitudinal fasciculus
- The medial vestibular nucleus
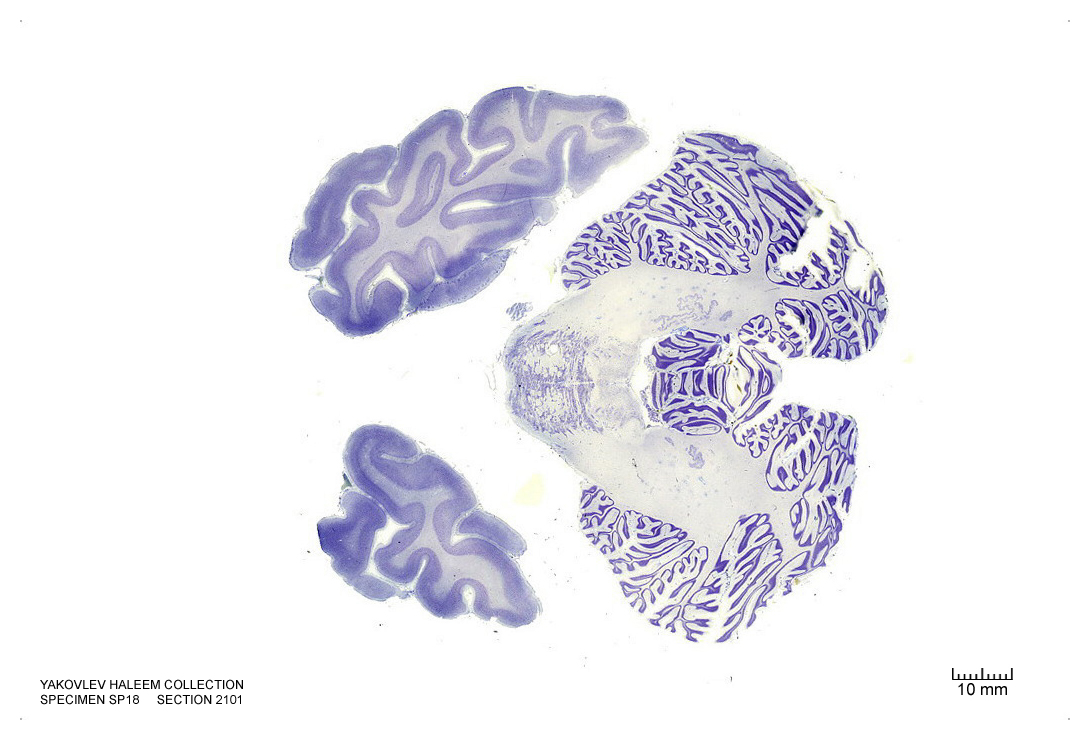
Figure 4.47: Horizontal section from The Human Brain Atlas at the Michigan State University Brain Biodiveristy Bank which acknowledges their support from the National Science Foundation.
In Figure 4.48, label the following structures:
- The solitary tract and nucleus
- The corticospinal fibers
- The cerebellum
- The vermis of the cerebellum
- The 4th ventricle
- The inferior cerebellar peduncle
- The medial vestibular nucleus
- The spinal trigeminal nucleus
- The spinal trigeminal tract
- The inferior cerebellar peduncle
- The cerebellar tonsil
- The medial longitudinal fasciculus
- The ventral cochlear nucleus
- The dorsal cochlear nucleus
- The hypoglossal nucleus
- The inferior vestibular nucleus
- The pontine nuclei
- The inferior olive
- The medial lemniscus
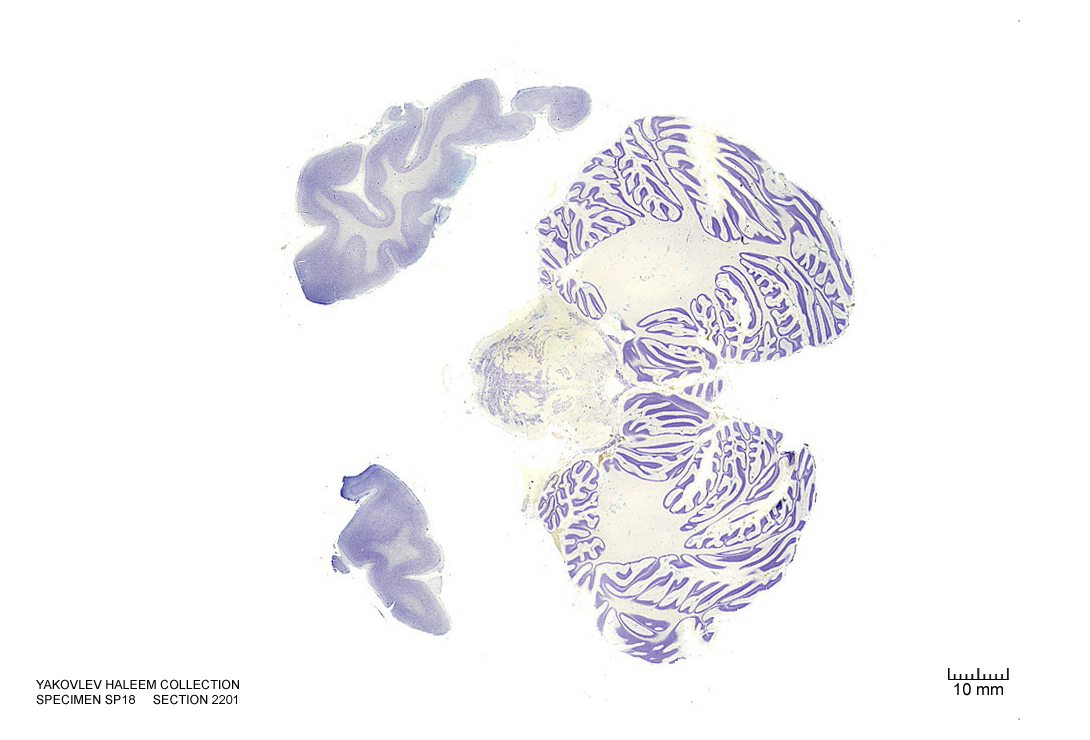
Figure 4.48: Horizontal section from The Human Brain Atlas at the Michigan State University Brain Biodiveristy Bank which acknowledges their support from the National Science Foundation.
In Figure 4.49, label the following structures:
- The solitary tract and nucleus
- The corticospinal fibers
- The cerebellum
- The 4th ventricle
- The inferior cerebellar peduncle
- The inferior vestibular nucleus
- The spinal trigeminal tract
- The inferior cerebellar peduncle
- The cerebellar tonsil
- The medial longitudinal fasciculus
- The ventral cochlear nucleus
- The dorsal cochlear nucleus
- The hypoglossal nucleus
- The inferior vestibular nucleus
- The pontine nuclei
- The inferior olive
- The medial lemniscus
- The choroid plexus
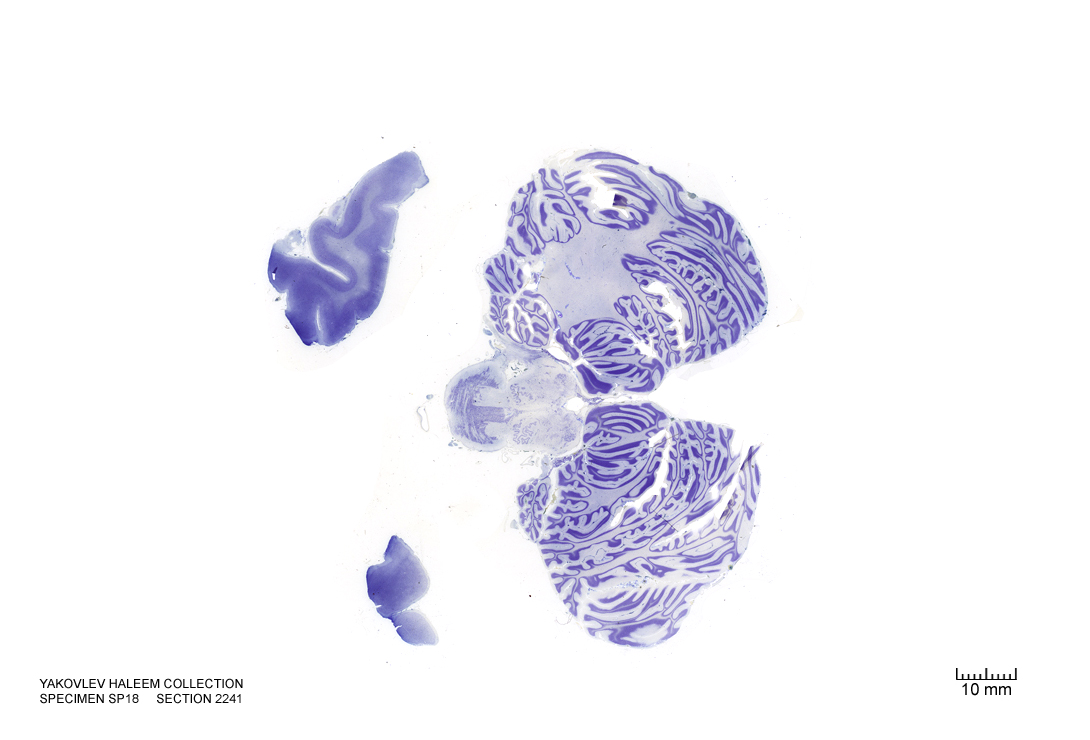
Figure 4.49: Horizontal section from The Human Brain Atlas at the Michigan State University Brain Biodiveristy Bank which acknowledges their support from the National Science Foundation.
In Figure 4.50, label the following structures:
- The corticospinal fibers
- The cerebellum
- The 4th ventricle
- The inferior cerebellar peduncle
- The inferior vestibular nucleus
- The cerebellar tonsil
- The medial longitudinal fasciculus
- The ventral cochlear nucleus
- The hypoglossal nucleus
- The inferior vestibular nucleus
- The pontine nuclei
- The inferior olive
- The medial lemniscus
- The choroid plexus
- The dorsal cochlear nucleus
- The external cuneate nucleus
- The dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus
- The solitary nucleus
- The hypoglossal nucleus
- The spinal trigeminal nucleus
- The spinal trigeminal tract
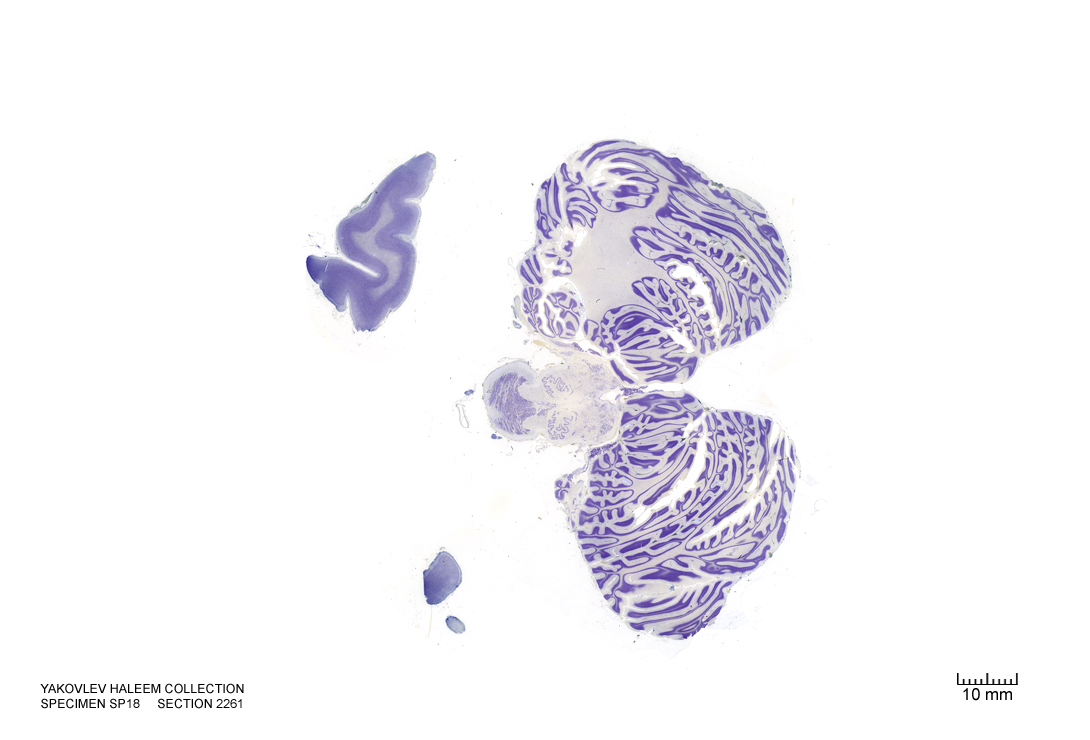
Figure 4.50: Horizontal section from The Human Brain Atlas at the Michigan State University Brain Biodiveristy Bank which acknowledges their support from the National Science Foundation.
In Figure 4.51, label the following structures:
- The corticospinal fibers
- The cerebellum
- The 4th ventricle
- The inferior cerebellar peduncle
- The inferior vestibular nucleus
- The cerebellar tonsil
- The cuneate nucleus
- The external cuneate nucleus
- The vestibulocochlear nerve
- The medial longitudinal fasciculus
- The dorsal cochlear nucleus
- The hypoglossal nucleus
- The inferior vestibular nucleus
- The medial lemniscus
- The choroid plexus
- The dorsal cochlear nucleus
- The dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus
- The solitary nucleus
- The spinal trigeminal nucleus
- The spinal trigeminal tract
- The solitary tract
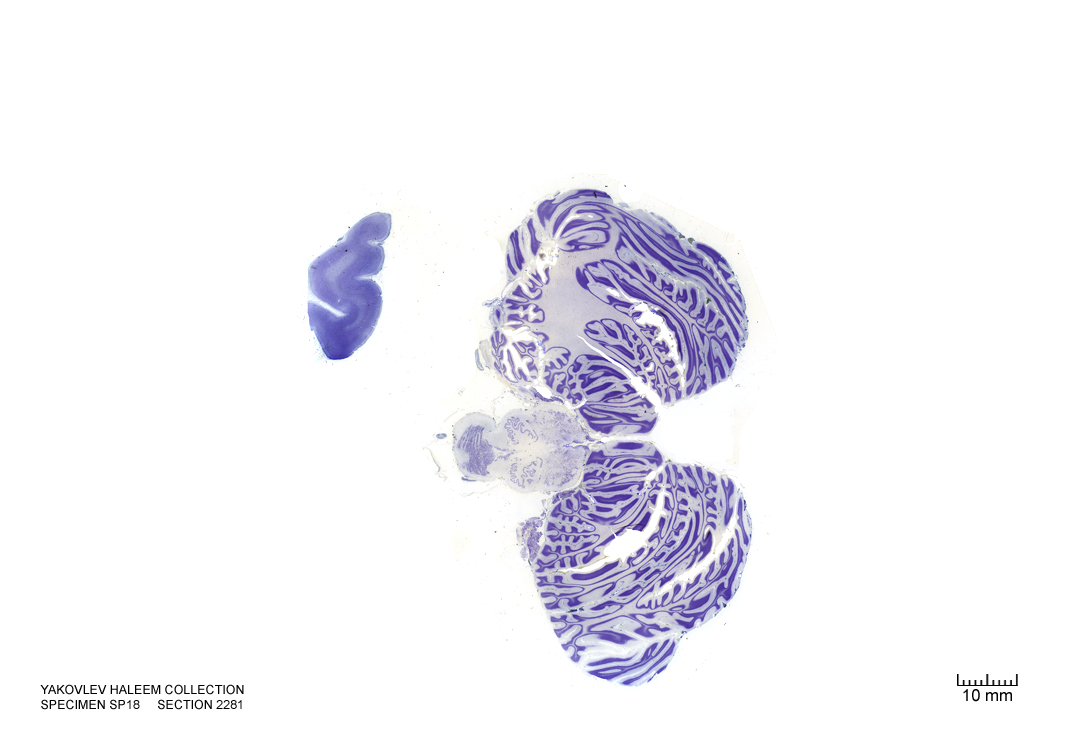
Figure 4.51: Horizontal section from The Human Brain Atlas at the Michigan State University Brain Biodiveristy Bank which acknowledges their support from the National Science Foundation.
In Figure 4.52, label the following structures:
- The corticospinal fibers
- The cerebellum
- The 4th ventricle
- The inferior cerebellar peduncle
- The inferior vestibular nucleus
- The cerebellar tonsil
- The external cuneate nucleus
- The medial longitudinal fasciculus
- The hypoglossal nucleus
- The decussatin of the medial lemniscus
- The dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus
- The solitary nucleus
- The spinal trigeminal nucleus
- The spinal trigeminal tract
- The solitary tract
- The lateral reticular nucleus
- The gracile nucleus
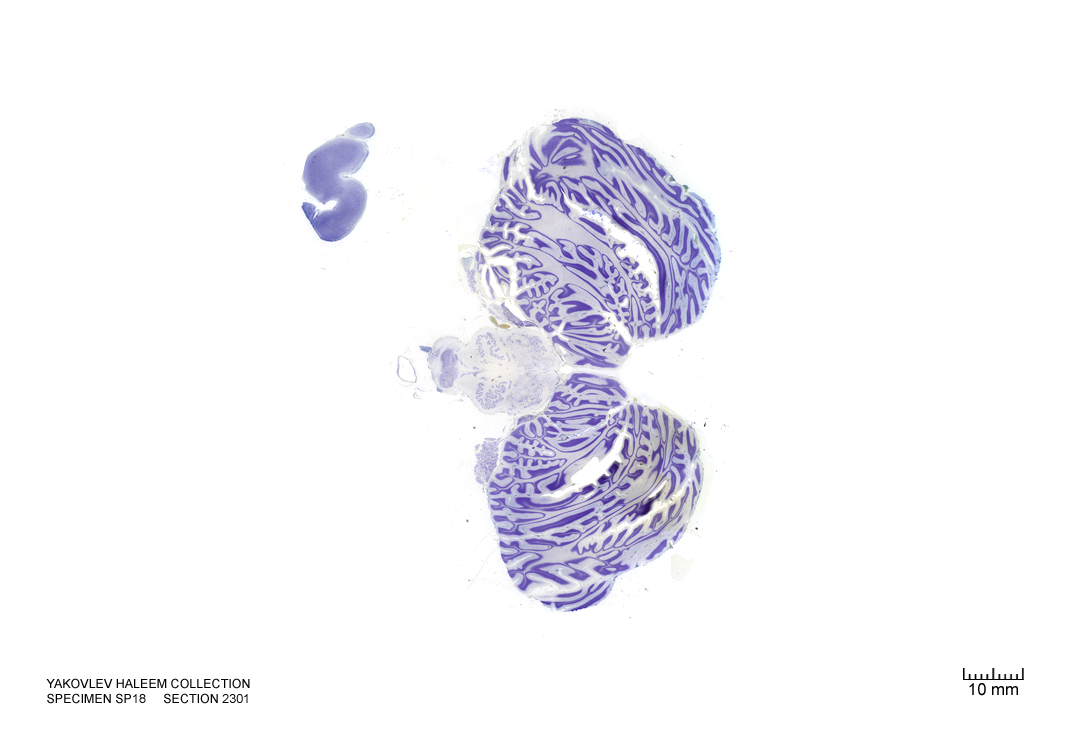
Figure 4.52: Horizontal section from The Human Brain Atlas at the Michigan State University Brain Biodiveristy Bank which acknowledges their support from the National Science Foundation.
In Figure 4.53, label the following structures:
- The corticospinal fibers
- The cerebellum
- The 4th ventricle
- The inferior cerebellar peduncle
- The inferior vestibular nucleus
- The cerebellar tonsil
- The external cuneate nucleus
- The medial longitudinal fasciculus
- The hypoglossal nucleus
- The decussatin of the medial lemniscus
- The dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus
- The solitary nucleus
- The spinal trigeminal nucleus
- The spinal trigeminal tract
- The solitary tract
- The lateral reticular nucleus
- The gracile nucleus
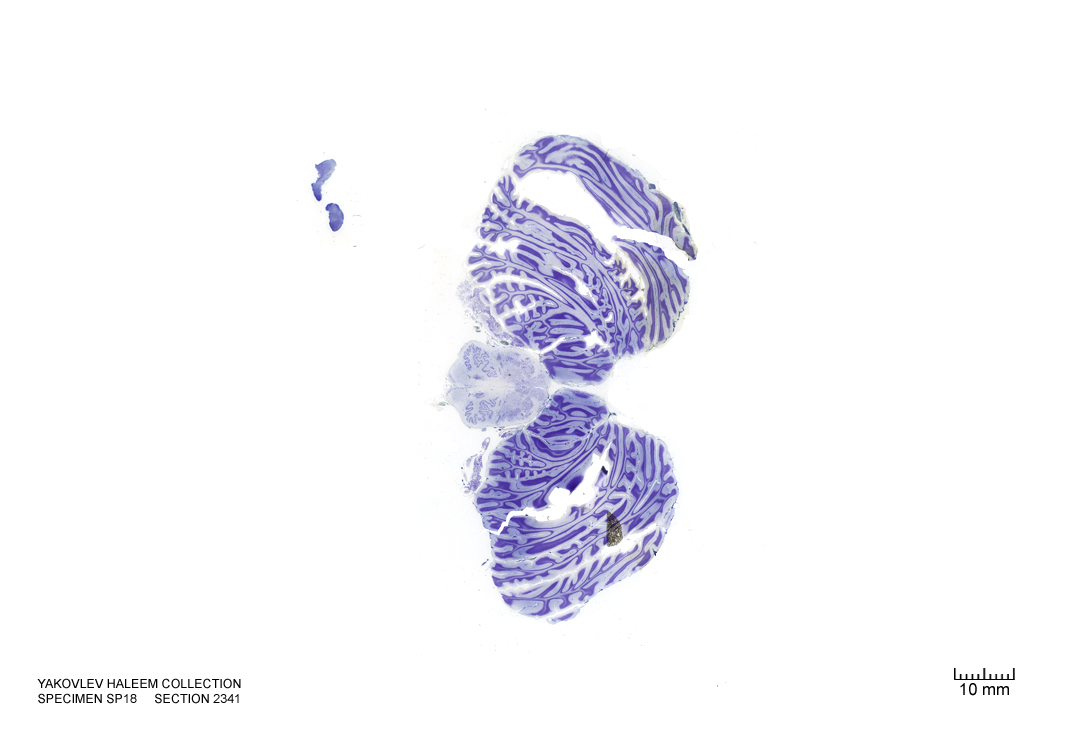
Figure 4.53: Horizontal section from The Human Brain Atlas at the Michigan State University Brain Biodiveristy Bank which acknowledges their support from the National Science Foundation.
In Figure 4.54, label the following structures:
- The corticospinal fibers
- The pyramids
- The accessory nucleus
- The cerebellum
- The 4th ventricle
- The inferior cerebellar peduncle
- The inferior vestibular nucleus
- The cerebellar tonsil
- The cuneate nucleus
- The medial longitudinal fasciculus
- The hypoglossal nucleus
- The decussatin of the medial lemniscus
- The solitary nucleus
- The spinal trigeminal nucleus
- The spinal trigeminal tract
- The solitary tract
- The lateral reticular nucleus
- The gracile nucleus
- The inferior cerebellar peduncle
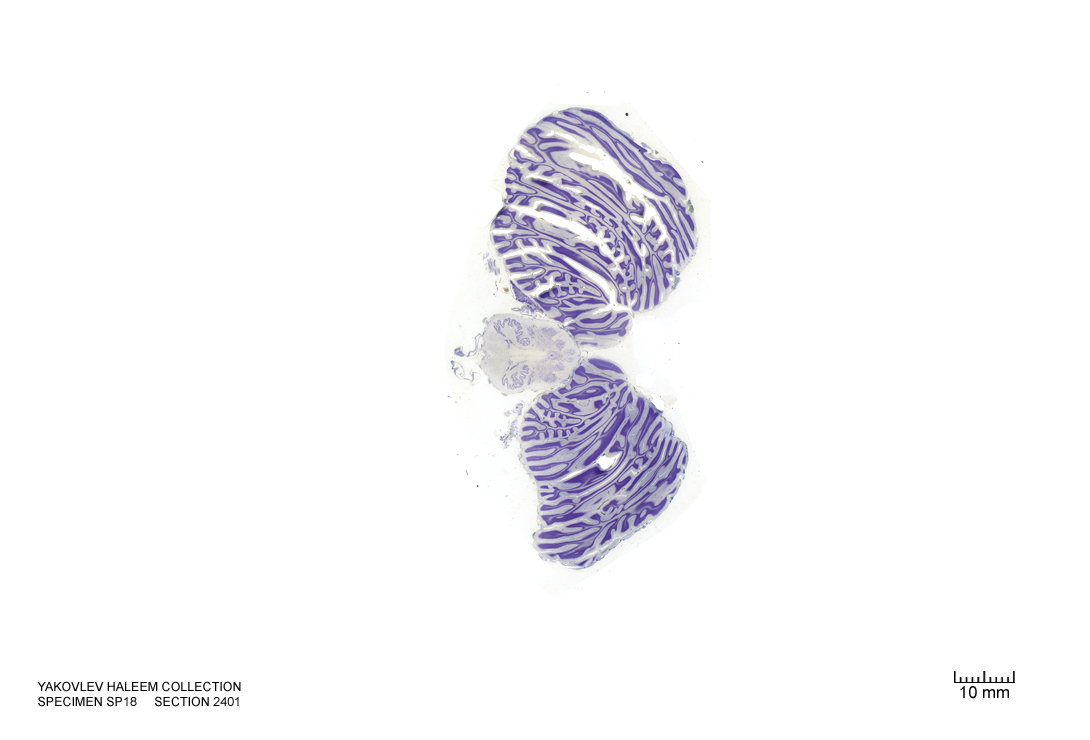
Figure 4.54: Horizontal section from The Human Brain Atlas at the Michigan State University Brain Biodiveristy Bank which acknowledges their support from the National Science Foundation.
In Figure 4.55, label the following structures:
- The pyramids
- The pyramidal decussation
- The accessory nucleus
- The cerebellum
- The 4th ventricle
- The inferior cerebellar peduncle
- The inferior vestibular nucleus
- The cerebellar tonsil
- The cuneate nucleus
- The cuneate fasciculus
- The medial longitudinal fasciculus
- The spinal trigeminal nucleus
- The spinal trigeminal tract
- The solitary tract
- The lateral reticular nucleus
- The gracile nucleus
- The gracile fasciculus
- The medial motor nuclei

Figure 4.55: Horizontal section from The Human Brain Atlas at the Michigan State University Brain Biodiveristy Bank which acknowledges their support from the National Science Foundation.
In Figure 4.56, label the following structures:
- The pyramidal decussation
- The accessory nucleus
- The cerebellum
- The cerebellar tonsil
- The cuneate nucleus
- The cuneate fasciculus
- The spinal trigeminal nucleus
- The substantia gelatinosa
- The lateral reticular nucleus
- The gracile nucleus
- The gracile fasciculus
- The medial motor nuclei
- The central grey

Figure 4.56: Horizontal section from The Human Brain Atlas at the Michigan State University Brain Biodiveristy Bank which acknowledges their support from the National Science Foundation.