3 Surface Anatomy Of The Brain
In this laboratory session, we will study the surface anatomy of the human brain. Below, you will be presented with a number of figures and asked to label or color certain structures in each figure.
3.1 A Dorsal View Of A Human Brain.
- Write “ANTERIOR’ and “POSTERIOR“ next to the arrowhead pointing in the corresponding direction:
- Write “LH“ over the left hemisphere and “RH“ over the right hemisphere in figure 1 below.
- Mark the longitudinal cerebral fissure with a sequence of “x”’s
Figure 3.1: A dorsal view of a human brain.
3.2 A Dorso-Lateral View Of A Human Brain.
- Write “ANTERIOR’ and “POSTERIOR“ next to the arrowhead pointing in the corresponding direction
- Trace the Sylvian fissure using a black marker
- Trace the central sulcus from the midline to the Sylvian fissure using a black marker
Figure 3.2: A dorso-lateral view of a human brain.
3.3 A Lateral View Of A Human Brain.
- Write “ANTERIOR’ and “POSTERIOR“ next to the arrowhead pointing in the corresponding direction
- Write “DORSAL“ and “VENTRAL“ next to the arrowhead pointing in the corresponding direction
- Write “CEREBRUM“ and “CEREBELLUM“ next to the corresponding structures
- rite “BRAINSTEM“ next to the corresponding structure
- Write “OLFACTORY BULB“ next to the corresponding structure
Figure 3.3: A lateral view of a human brain.
3.4 A Ventral View Of A Human Brain.
- Write “LH“ over the left hemisphere and “RH‘ over the right hemisphere in figure 1 below.
- Write “LCblH“ over the left hemisphere of the cerebellum and “RCblH‘ over the right cerebellar hemisphere in the figure below.
- Write “Pons“ over the corresponding structure in the figure below.
- Write “MO“ denoting the medulla oblongata over the corresponding structure in the figure below.
- Write “ANTERIOR’ and “POSTERIOR“ next to the arrowhead pointing in the corresponding direction.
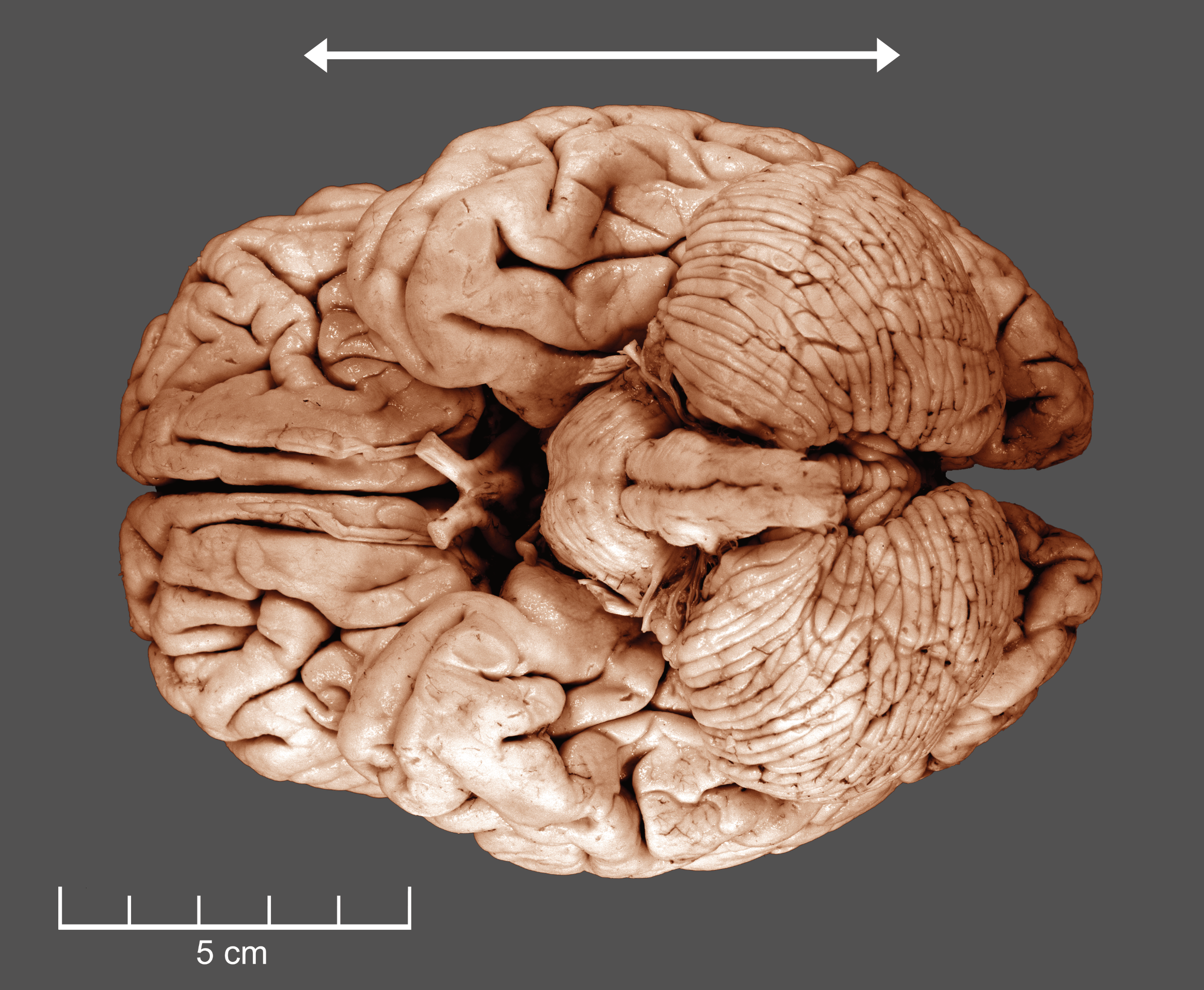
Figure 3.4: A ventral view of a human brain.
3.5 A Lateral View Of The Human Brain.
- Color the frontal lobe red
- Color the temporal lobe green
- Color the parietal lobe yellow
- Color the occipital lobe blue
- Mark the central sulcus with a sequence of “o“’s
- Mark the Sylvian fissure with a sequence of “x”’s
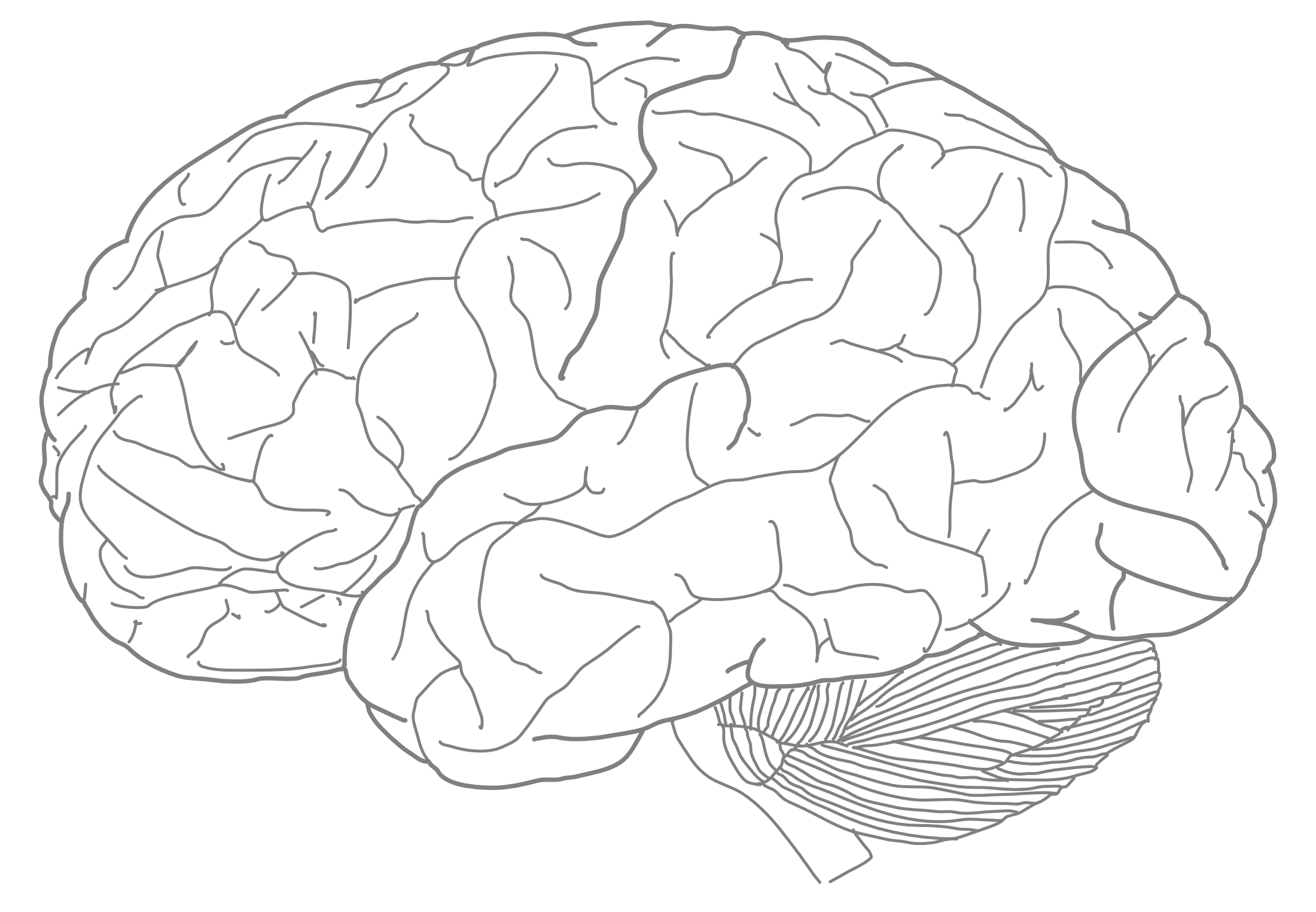
Figure 3.5: A lateral view of the major lobes of the human brain.
- Mark the central sulcus with a sequence of “o“’s.
- Mark the Sylvian fissure with a sequence of “x”’s.
- Color the precentral gyrus red.
- Color the postcentral gyrus green.
- Color the superior temporal gyrus blue.
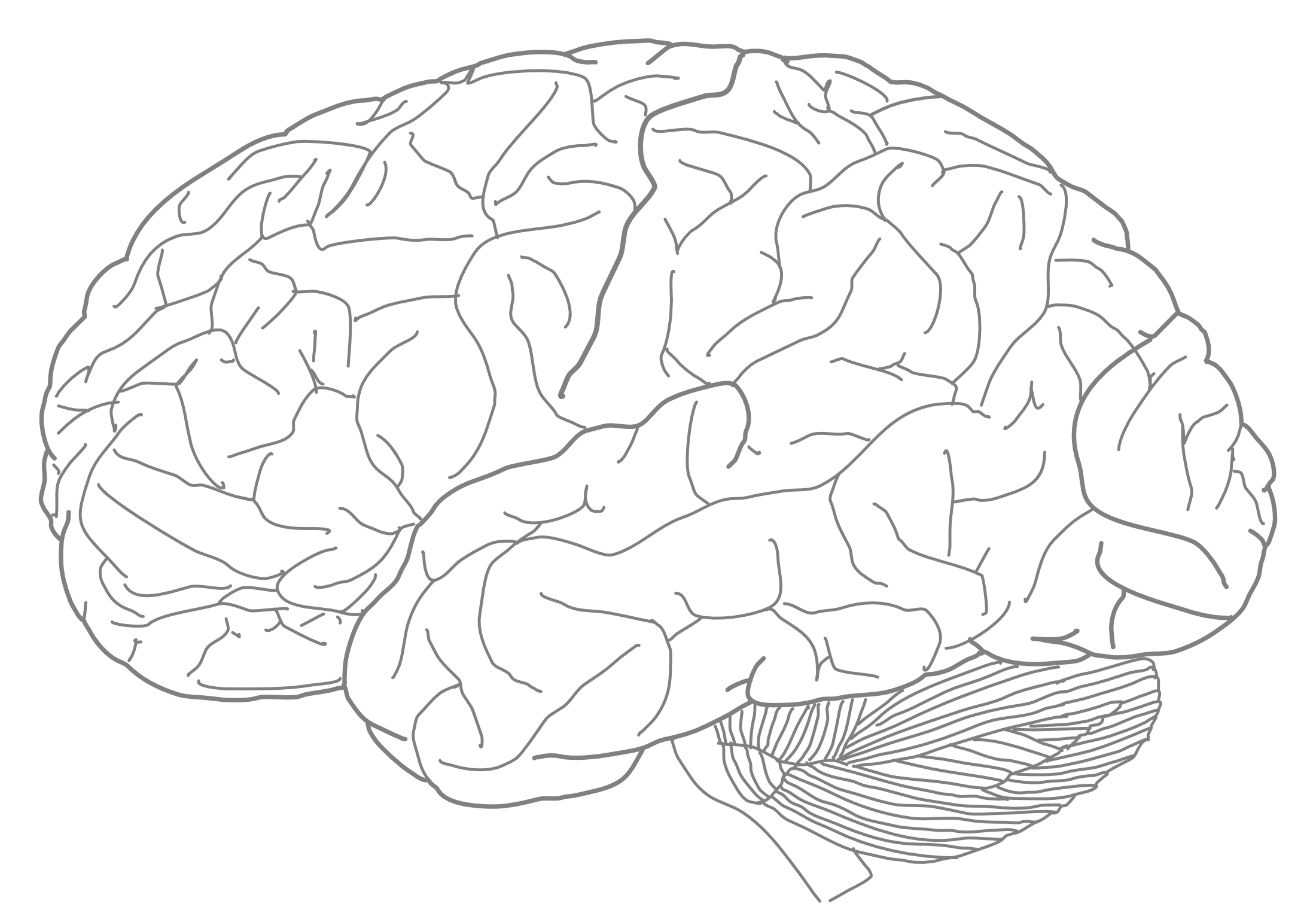
Figure 3.6: A lateral view of the major gyri of the human brain.
3.6 A Medial View Of The Human Brain.
- Color the septum pellucidum yellow
- Color the thalamus blue
- Color the hypothalamus grey
- Color the pons red
- Color the medulla oblongata green
- Color the tectum yellow
- Color the tegmentum grey
- Color the pineal body red
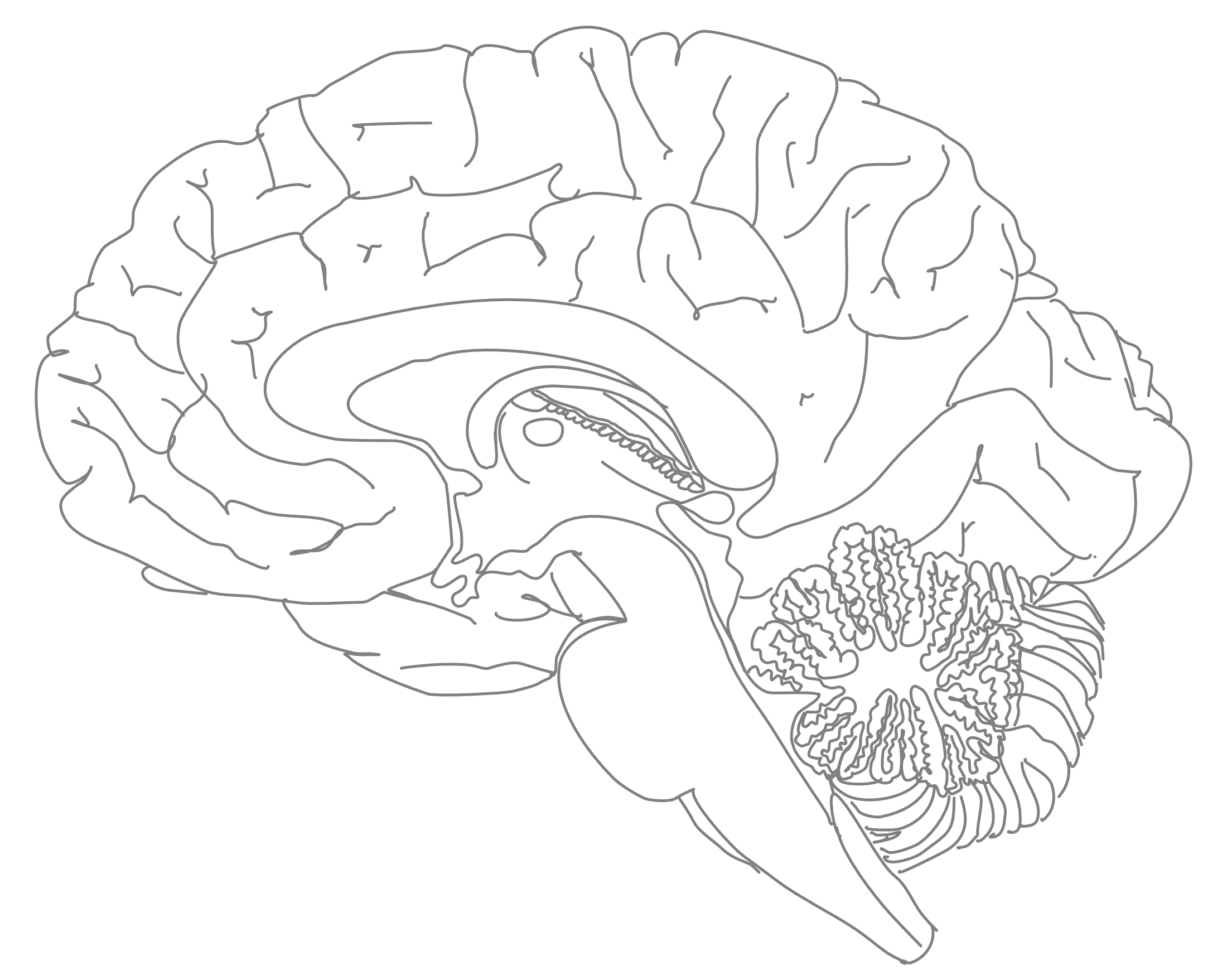
Figure 3.7: A medial view of the human brain (#1).
- Color the cingulate gyrus green
- Color the corpus callosum red
- Color the fornix yellow
- Color the olfactory bulb blue
- Color the optic chiasm grey
Figure 3.8: A medial view of a human brain (#2).
- Color the third ventricle green
- Color the aqueduct red
- Color the fourth ventricle blue
- Color the spinal call yellow
Figure 3.9: A medial view of a human brain (#3).
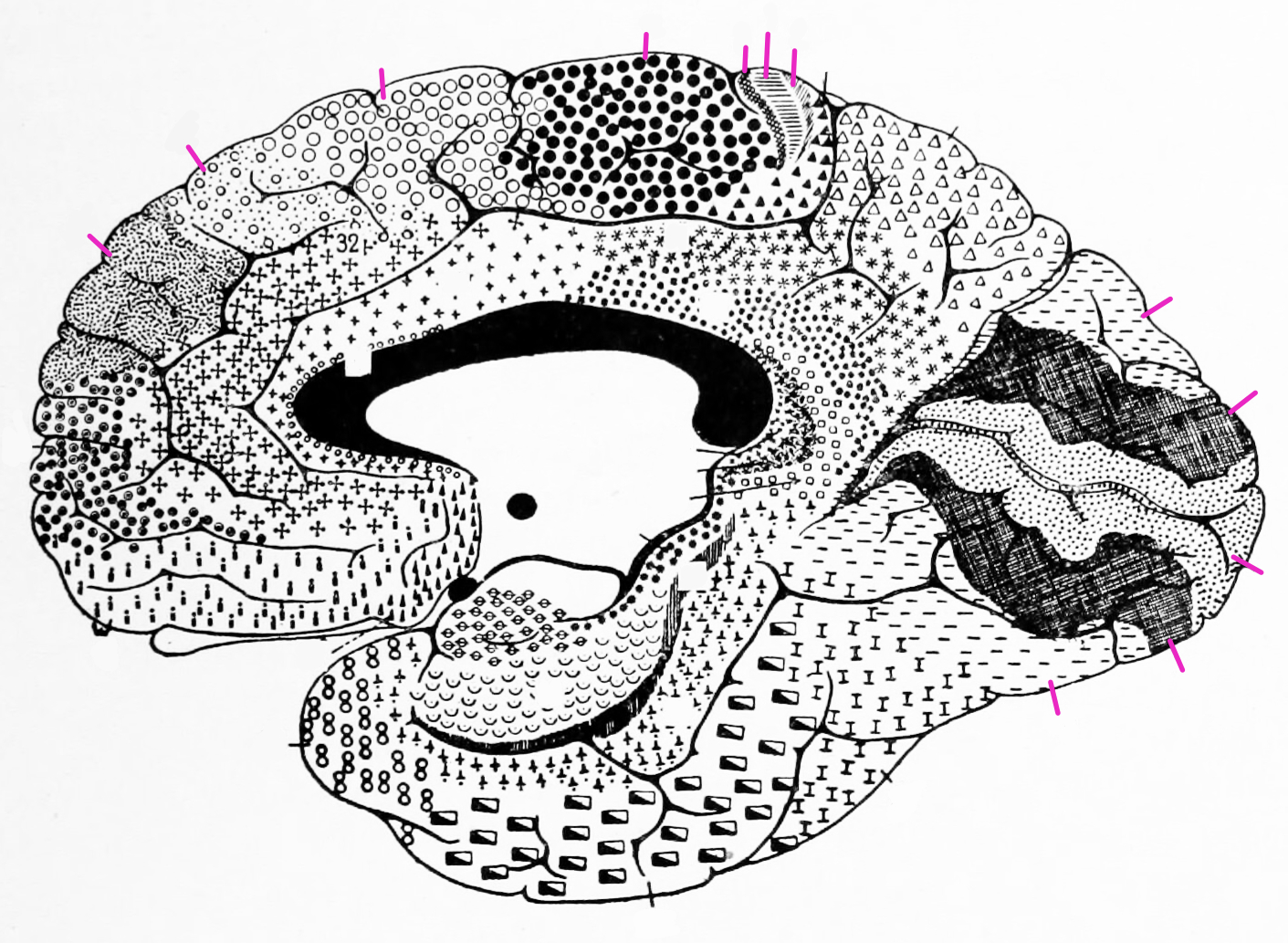
3.7 Cytoarchitectonic Areas According To Brodmann
- Label the highlighted areas with the corresponding numbers given by Broadmann.
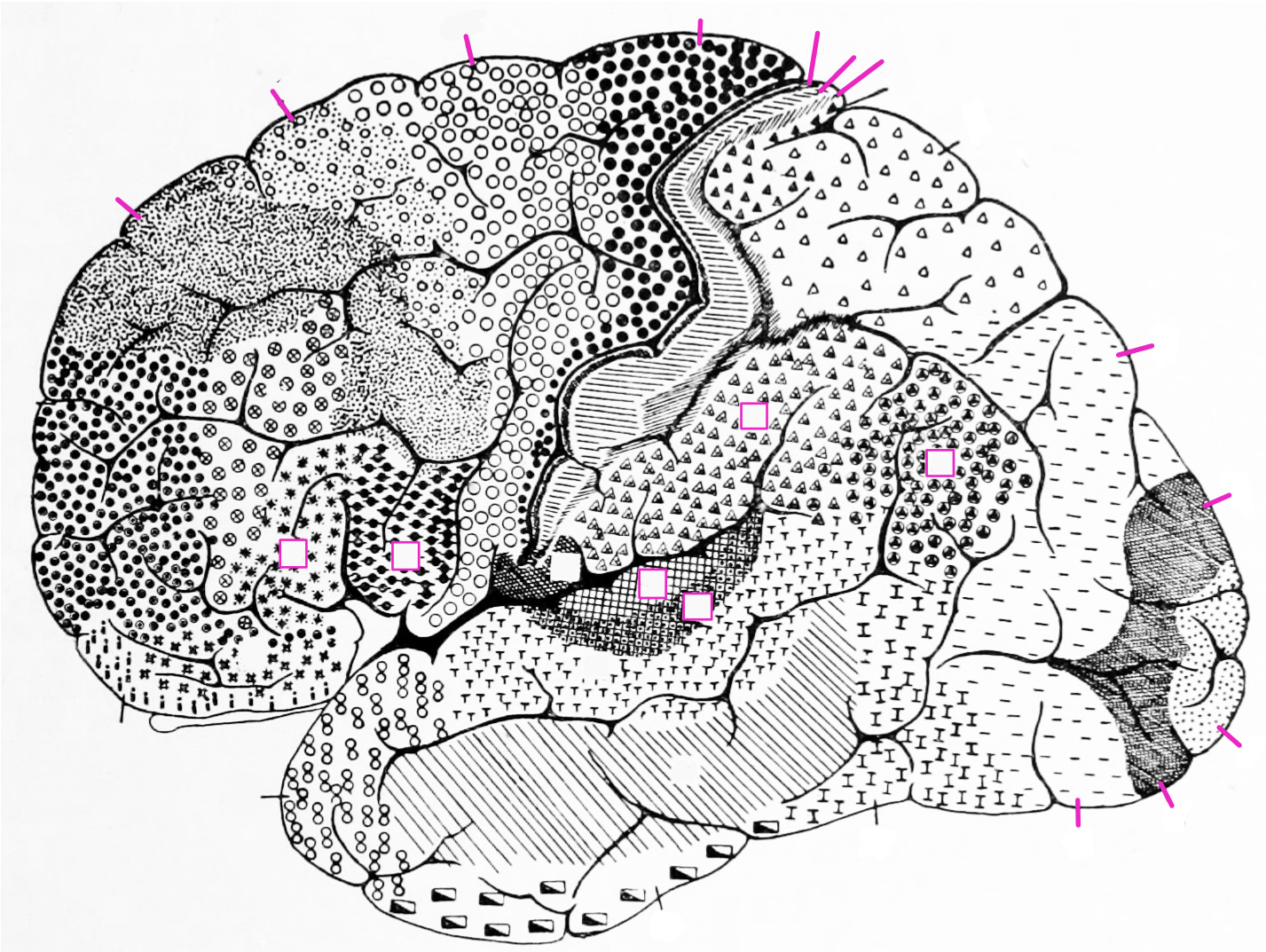
Figure 3.10: A lateral view of the cytoarchitectonic areas of the human brain according to Brodmann.
- Label the highlighted Brodamann areas with the corresponding numbers.